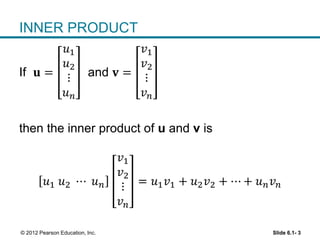
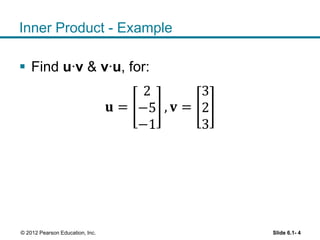
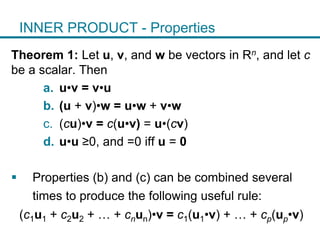
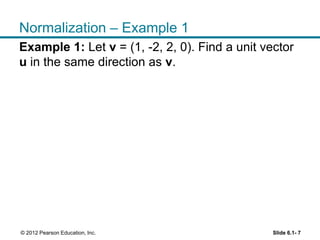
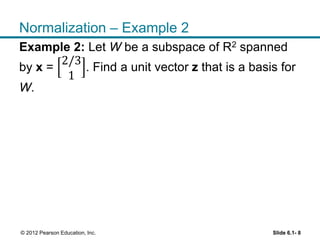
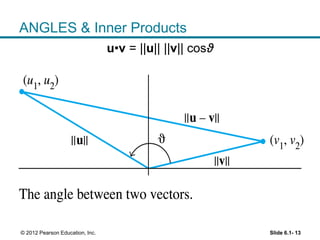
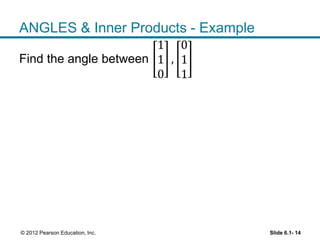
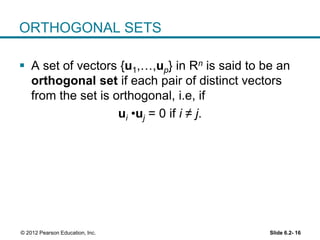
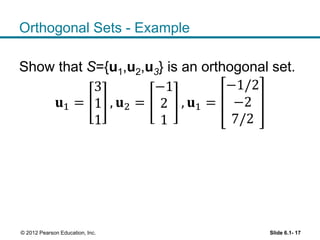
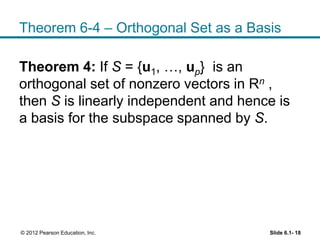
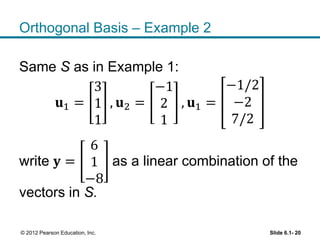
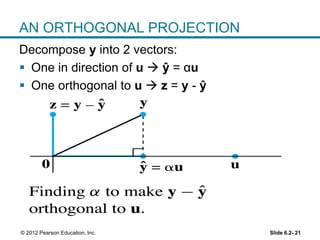
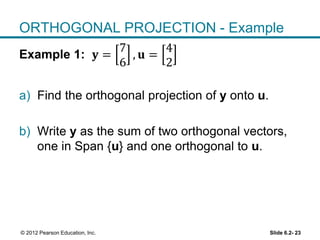
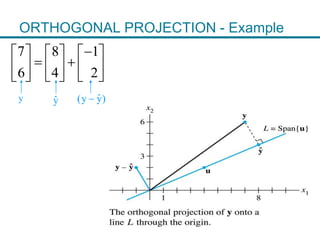
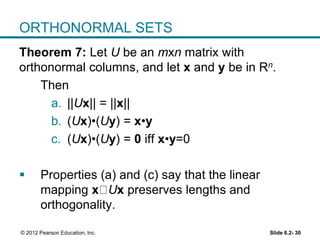
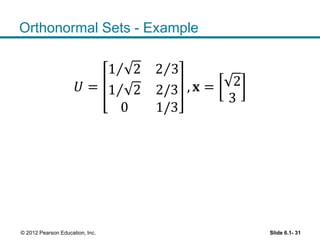
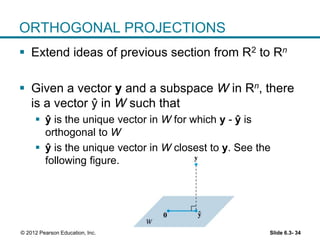
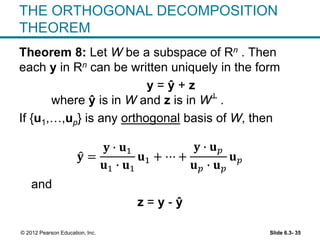
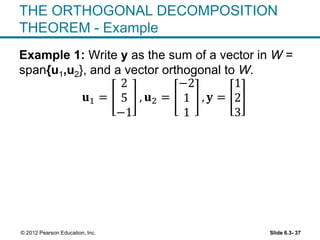
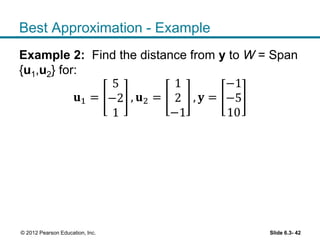
1. The orthogonal decomposition theorem states that any vector y in Rn can be written uniquely as the sum of a vector ŷ in a subspace W and a vector z orthogonal to W.
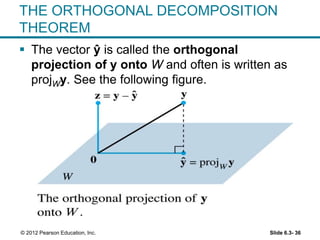
2. The vector ŷ is called the orthogonal projection of y onto W. It is the closest vector to y that lies in W.
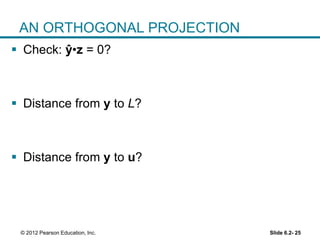
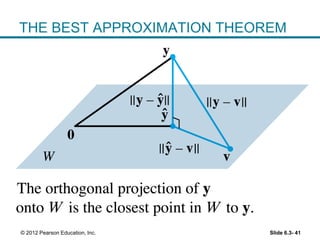
3. The best approximation theorem states that the orthogonal projection ŷ provides the best or closest approximation of y using only vectors that lie in the subspace W. The distance from y to ŷ is less than the distance from y to any other vector in