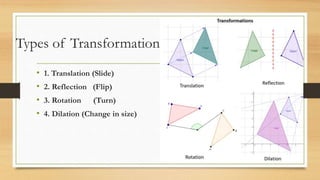
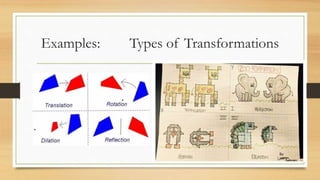
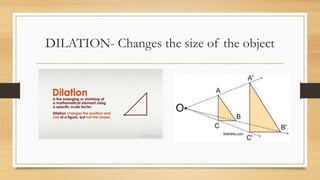
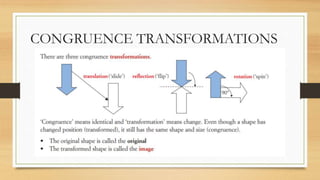
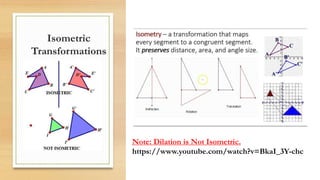
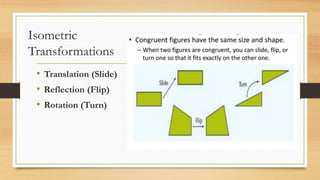
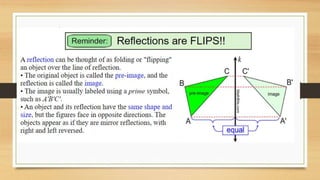
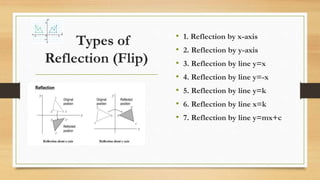
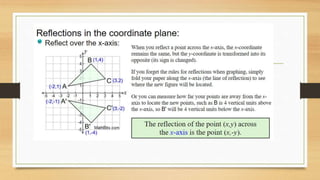
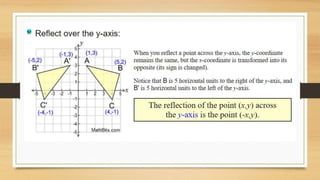
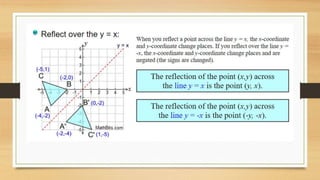
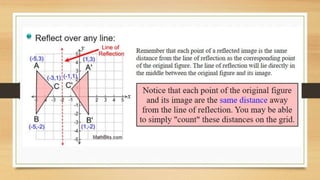
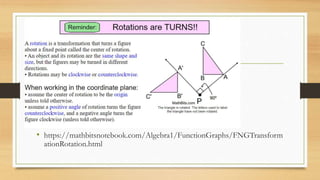
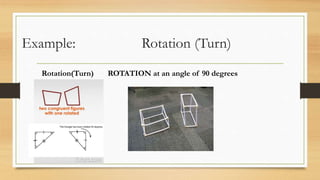
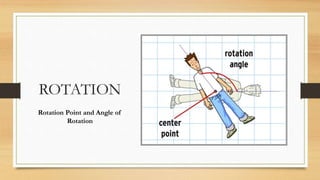
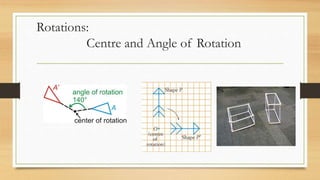
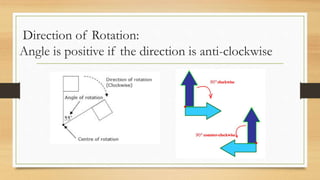
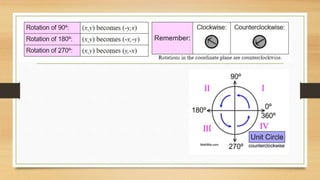
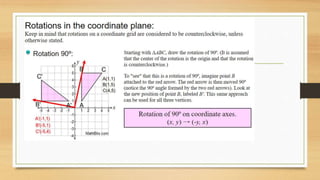
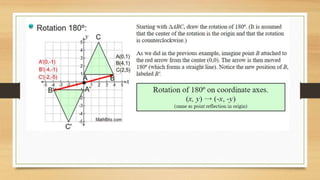
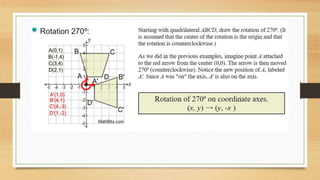
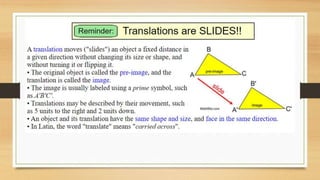
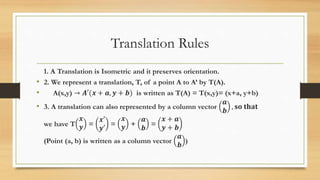
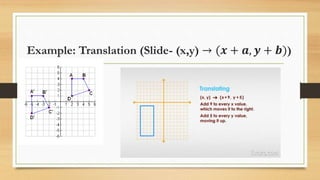
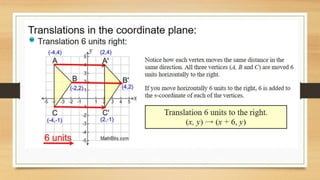
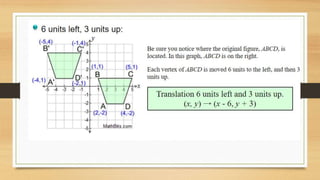
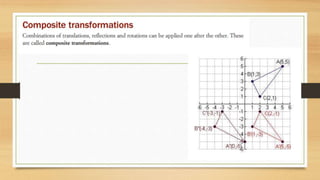
This document discusses different types of geometric transformations including translations, reflections, rotations, and dilations. It provides examples and notations for each type of transformation. Translations involve sliding an object along a vector, reflections involve flipping an object across a line, rotations involve turning an object around a fixed point, and dilations involve changing the size of an object. The document also discusses isometric transformations, lines of reflection, and applications of transformations including tessellations. Examples are provided to demonstrate different transformations and how to find equations of lines of reflection.