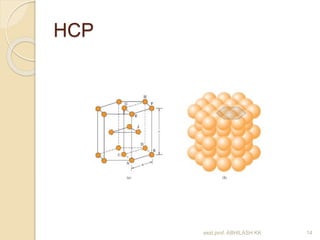
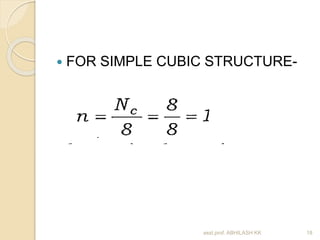
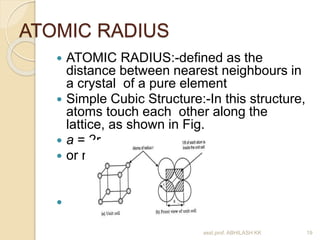
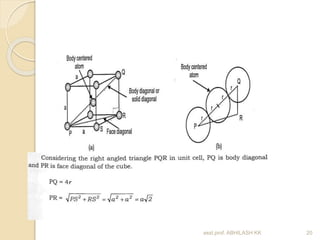
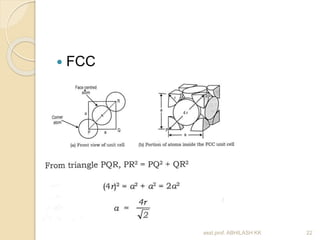
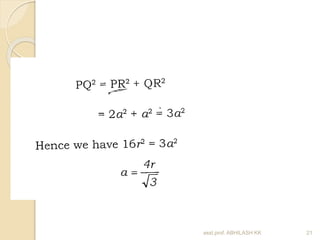This document discusses the structure of materials and crystallography. It describes different levels of structure like microscopic, sub-structure, and crystal structure. It also classifies materials based on their chemical makeup, atomic arrangement, and application. Key crystal structures discussed include simple cubic, body centered cubic, face centered cubic, and hexagonal close packed. The document defines concepts like unit cell, lattice points, coordination number, and atomic packing factor. It provides formulas to calculate atomic radius and number of atoms in unit cells for different crystal structures.