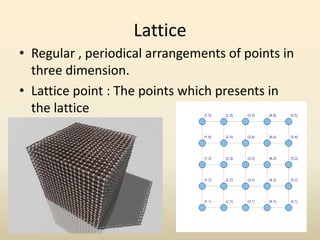
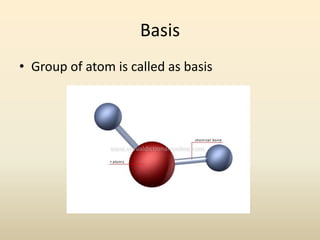
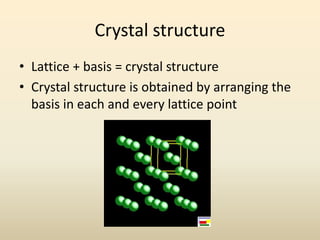
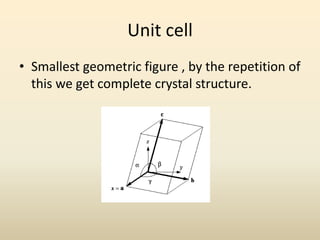
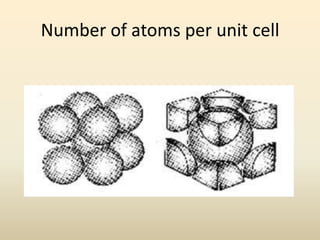
- A crystal structure is formed by arranging basis groups of atoms in a periodic three-dimensional lattice. The smallest repeating unit of a crystal structure is the unit cell.
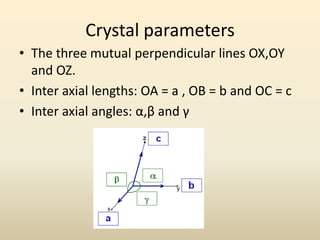
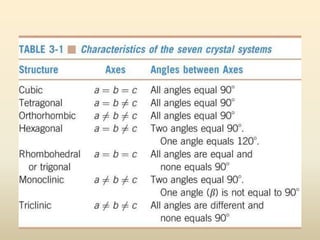
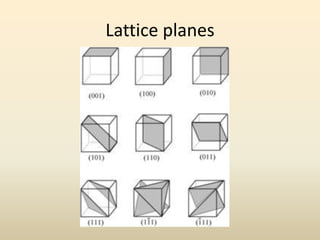
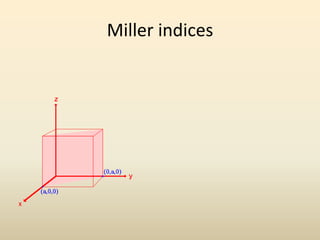
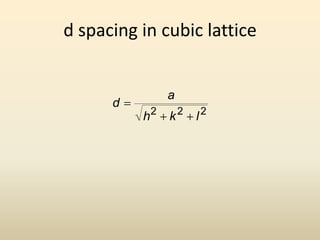
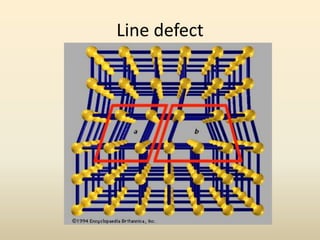
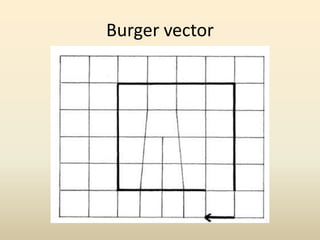
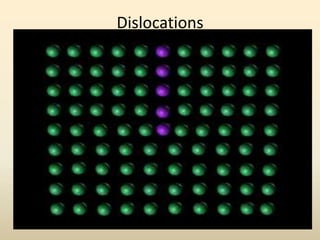
- Key parameters that define a crystal structure include the lattice type, basis, unit cell dimensions and angles, crystal system, and Miller indices of lattice planes.
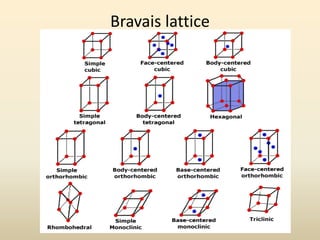
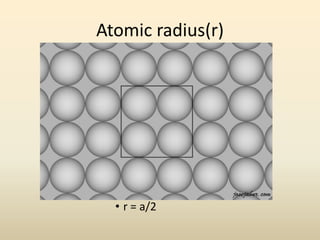
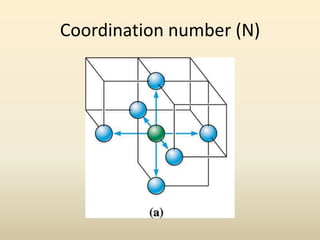
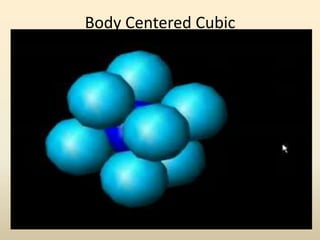
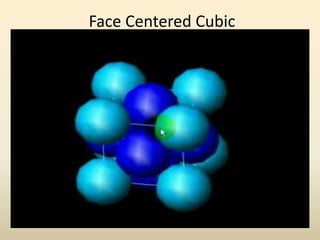
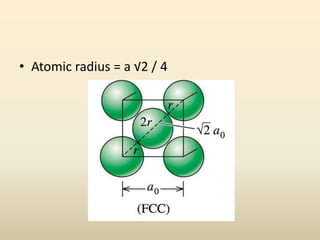
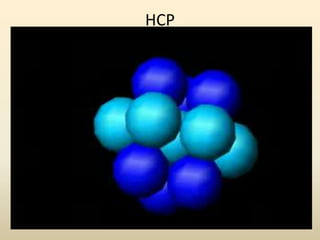
- Common crystal structures include simple cubic, body-centered cubic, face-centered cubic, and hexagonal close-packed. Polymorphism and allotropy refer to a material having more than one possible crystal structure.