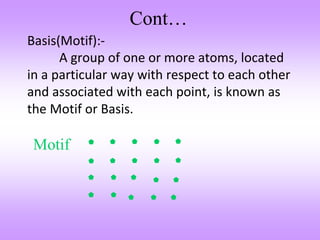
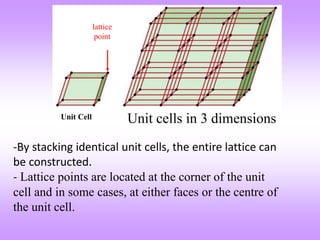
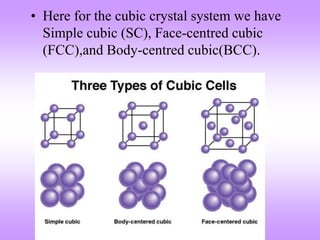
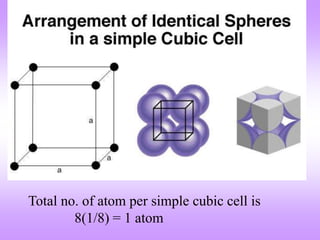
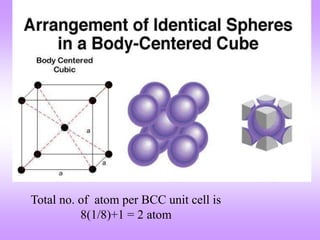
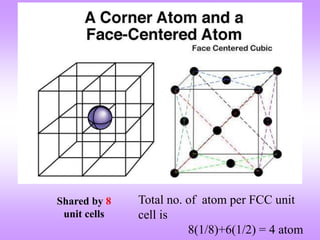
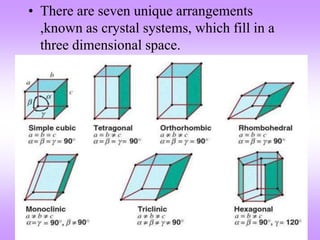
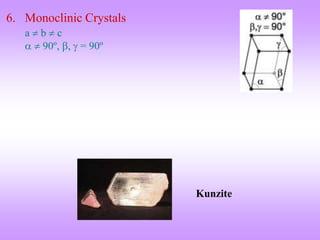
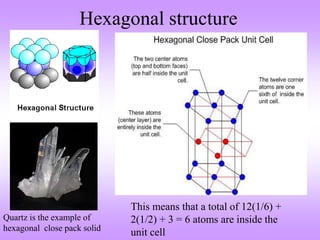
The document outlines the fundamentals of crystal structures, detailing the concepts of lattice and basis, and distinguishing between polycrystalline and single crystalline forms. It elaborates on unit cells and defines specific cubic crystal systems, including simple cubic, face-centered cubic, and body-centered cubic, along with their atomic compositions and seven distinct crystal systems. References for further reading include 'The Science and Engineering of Materials' by Donald R. Askeland and Pradeep P. Phule.