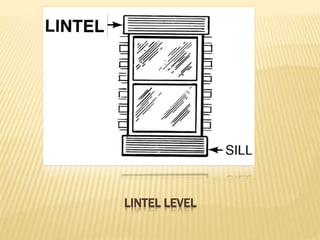
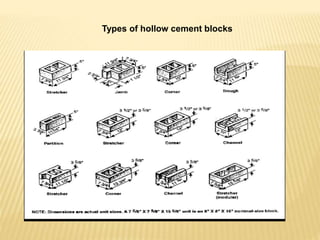
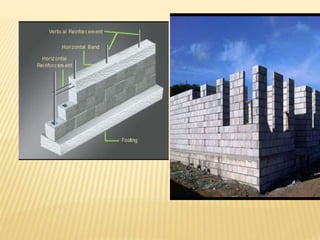
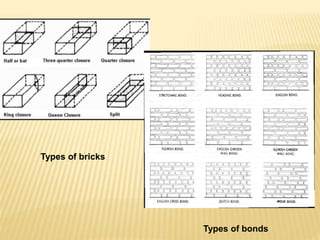
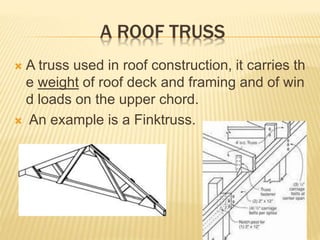
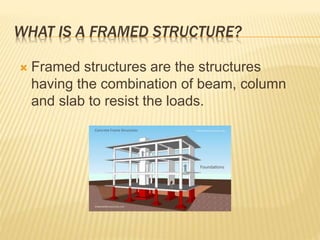
The document discusses various masonry structures and construction techniques. It describes cavity walls which have two skins separated by a hollow space to improve insulation. Stone cladding is discussed as a way to reduce construction costs. Various structural systems are also summarized like trusses which use triangles to provide rigidity, and cable-stayed bridges which use cables from towers to support the bridge deck. Framed structures are also introduced as using beams, columns, and slabs in combination to resist loads.