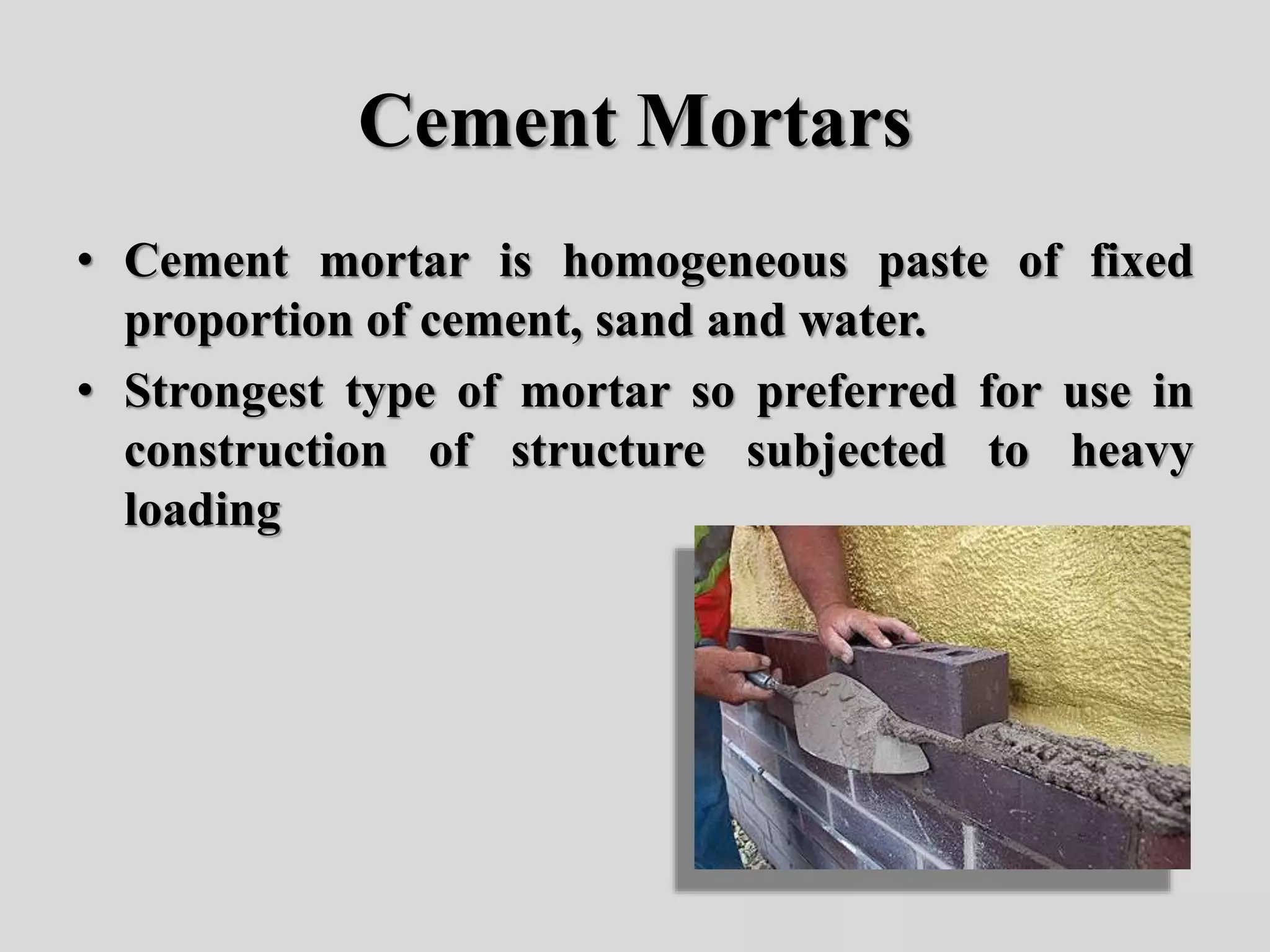
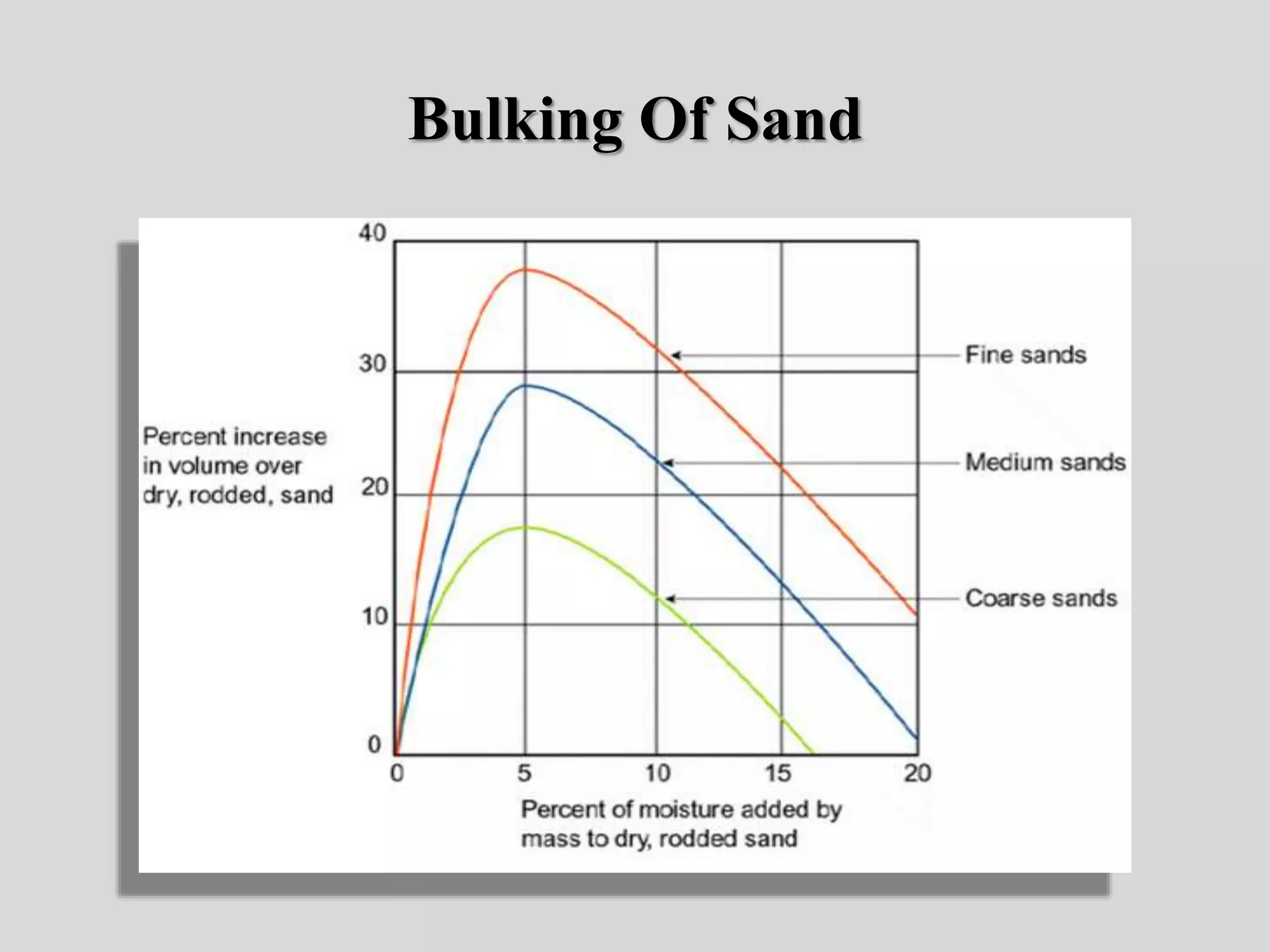
This document discusses mortars and plasters used in building construction. It defines mortars as mixtures used for joining bricks and stones, typically consisting of aggregates like sand and a binding material like lime or cement. It describes the different types of traditional mortars used in ancient structures like the pyramids of Egypt. It also outlines the key functions, properties, classifications, and uses of mortars and plasters. The document provides details on the preparation and curing of different types of mortars like lime, cement, and gauged mortars. It concludes with a section on sand and its classification according to origin and composition.