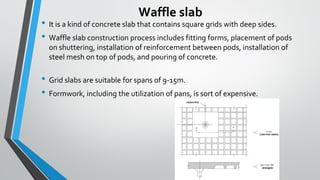
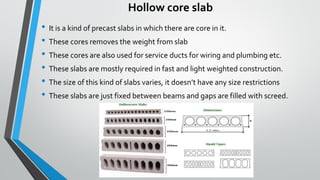
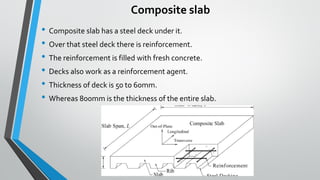
Slab is a thin concrete structure used for flooring that can be square, rectangular, or circular. Slabs vary in thickness from 4-6 inches depending on load and are made of cement, coarse aggregate, fine aggregate, and reinforcement bars. There are several types of slabs including one-way slabs which carry load in one direction, two-way slabs which carry load in two directions, joist slabs which have concrete ribs for support, and precast slabs which are constructed off-site and transported. Other slab types include flat plates, flat slabs, waffle slabs, hollow core slabs, and composite slabs which incorporate a steel deck.