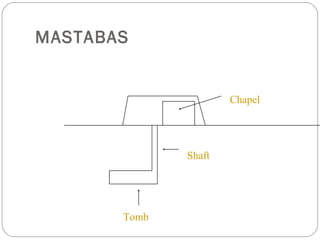
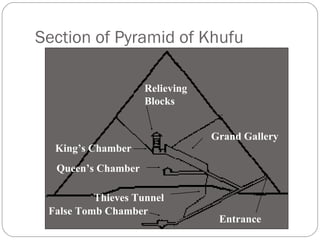
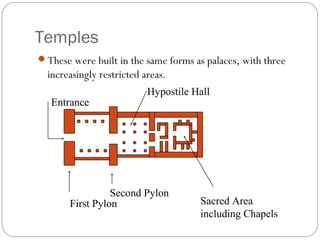
Egyptian architecture featured massive stone structures for temples and tombs, while domestic buildings used mud brick. Pyramids evolved from mastabas and step pyramids as ways to provide passage to the afterlife. The Great Pyramids of Giza, among the largest constructions ever built, housed tombs for pharaohs. Later pharaohs were buried in the Valley of the Kings, with hidden entrances and richly decorated tombs. Temples followed a structured layout and used light and shadow symbolically through clerestory windows and column placement.