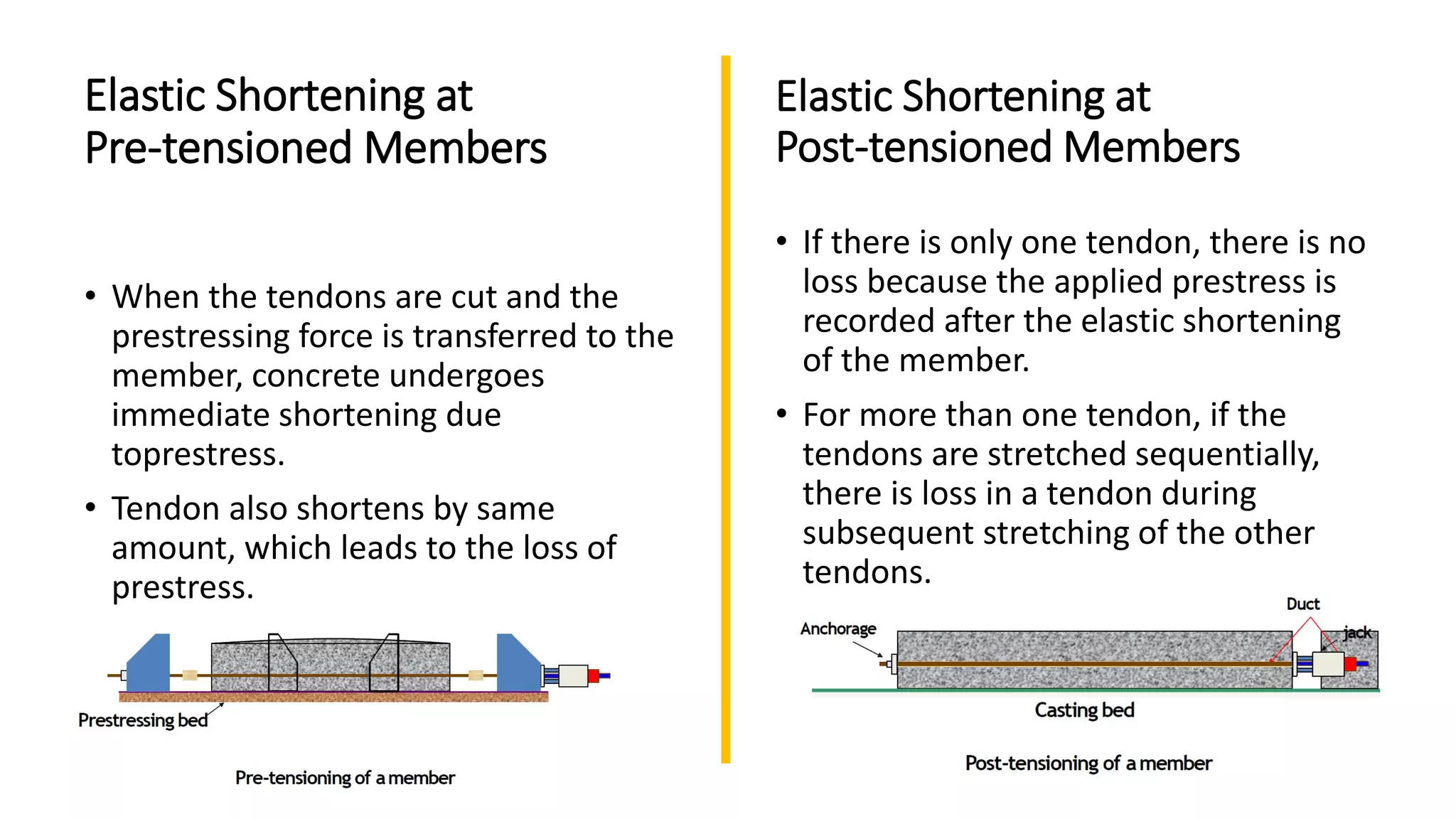
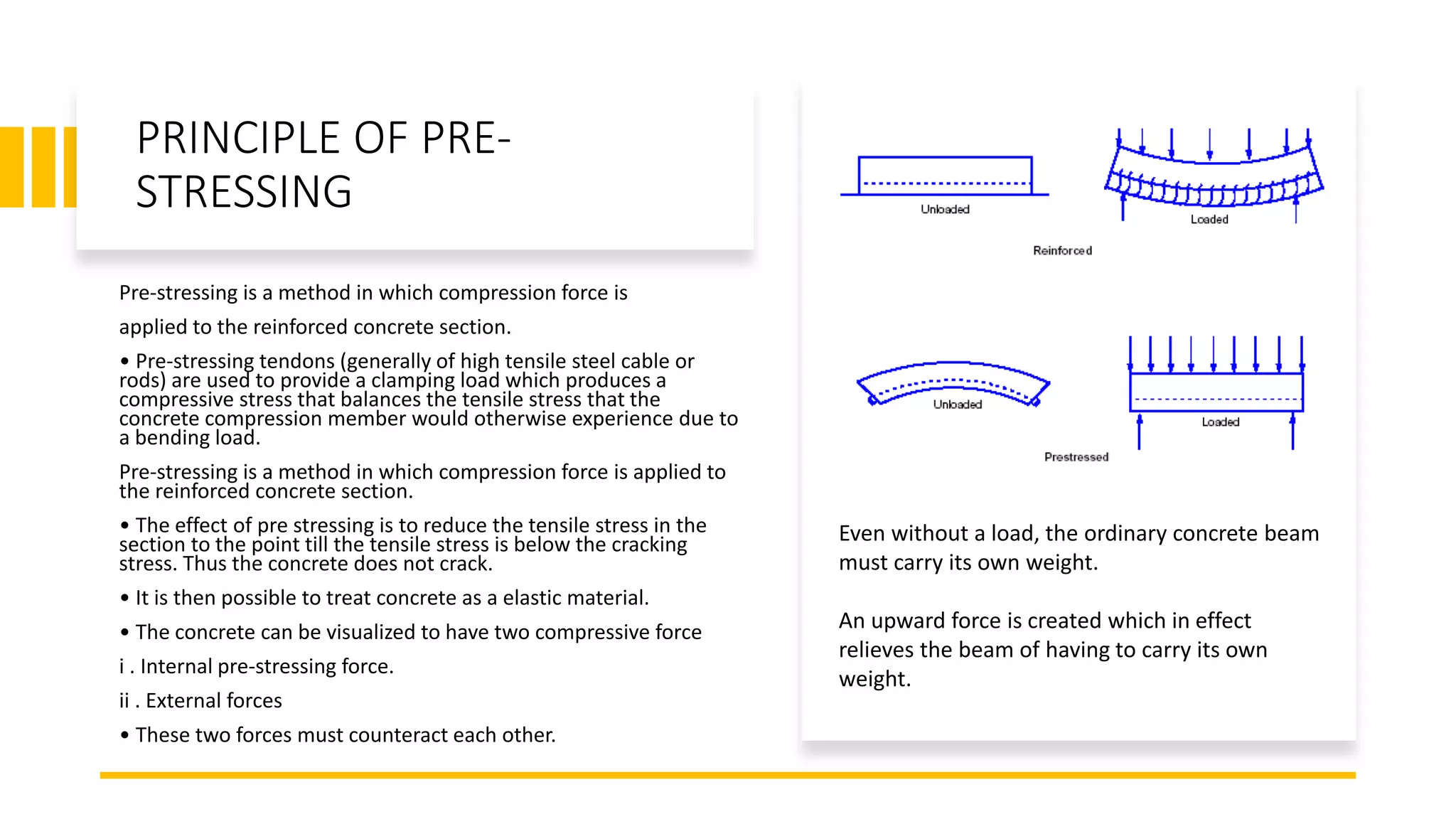
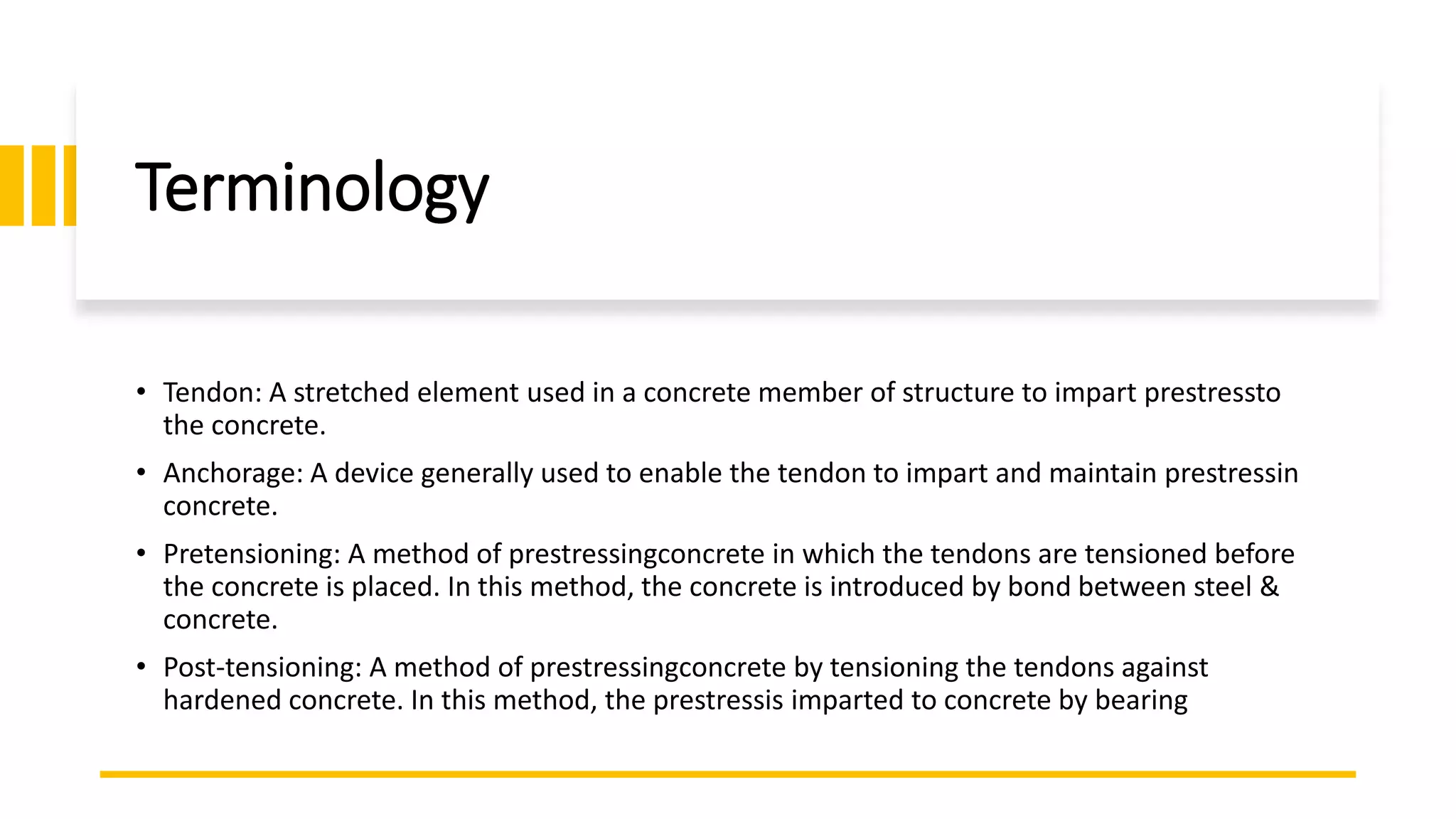
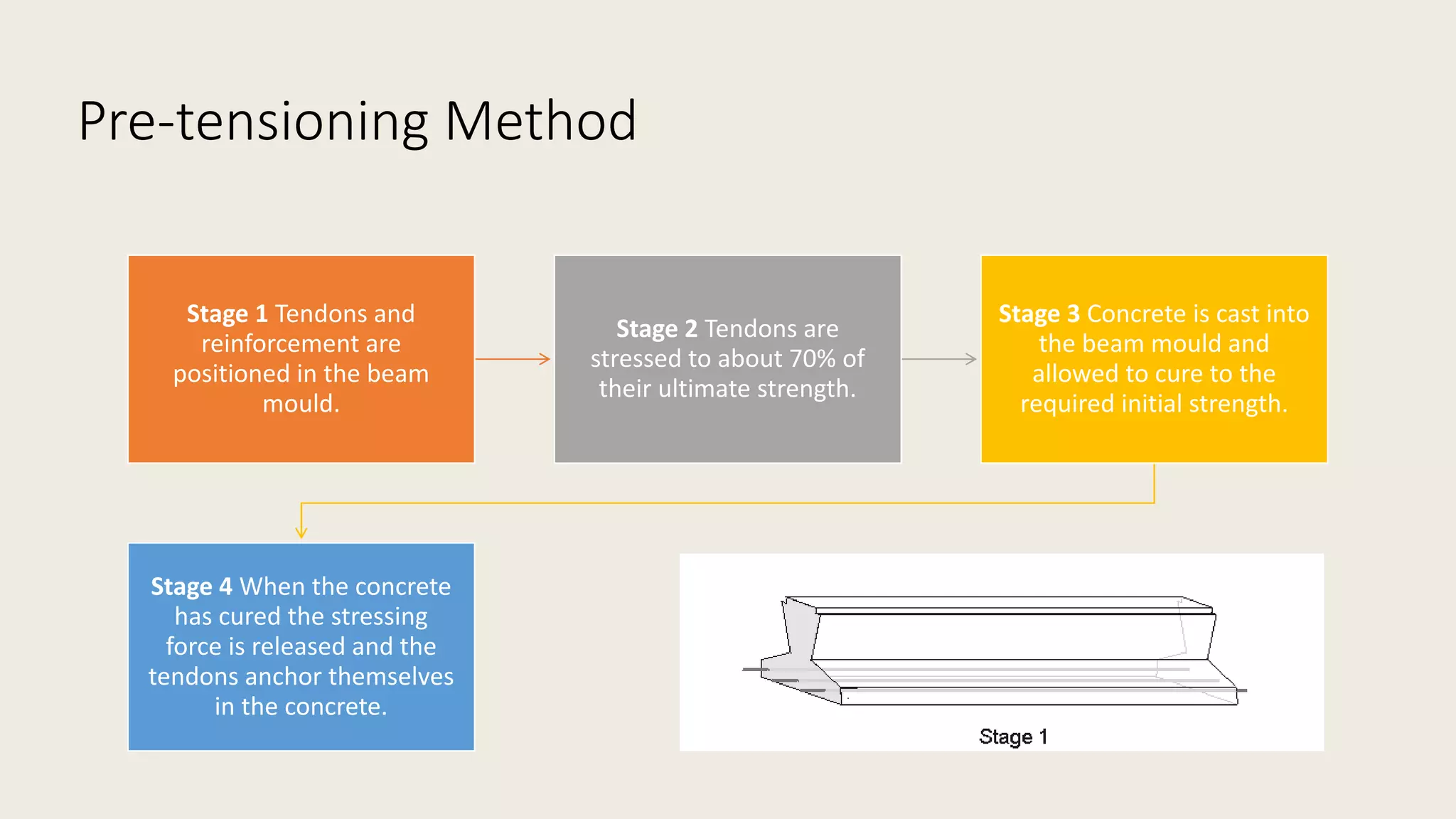
Prestressed concrete uses high-strength steel tendons or cables to put concrete members into compression prior to stresses from service loads being applied. This counters the tensile stresses induced by loading and improves the behavior of the concrete. There are two main methods - pretensioning and post-tensioning. Pretensioning involves stressing steel tendons before concrete is cast, while post-tensioning stresses steel tendons after the concrete has hardened. Losses in prestress over time include elastic shortening, anchorage slip, friction, creep, shrinkage, and steel relaxation. Proper material selection and design can minimize these losses and optimize the performance of prestressed concrete.















![Prestress loss
• loss in prestress is the difference between initial prestress and the effective
prestress.
• Loss of prestress affects
– the strength of member and
– member’s serviceability [ Stresses in Concrete, Cracking, Camber and Deflection]
It is difficult to generalize the amount of loss of prestress, because it is dependent
on so many Factors :
• The properties of concrete & steel.
• Curing & moisture condition.
• Magnitude & time of application of prestress.
• Process of prestress.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pre-stressedconcrete-210614044427/75/Pre-stressed-concrete-19-2048.jpg)