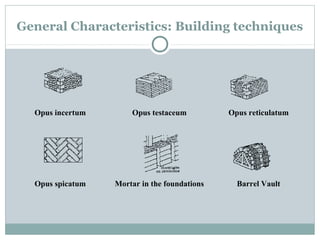
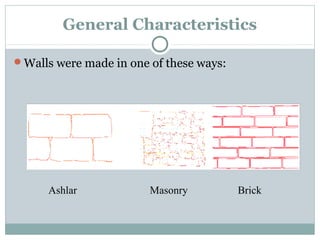
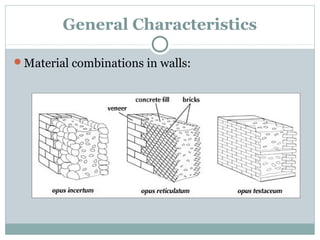
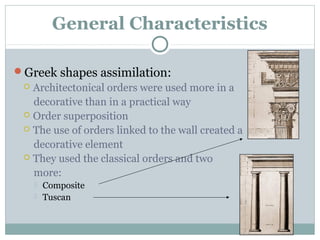
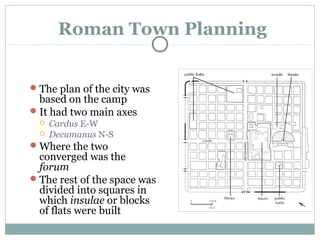
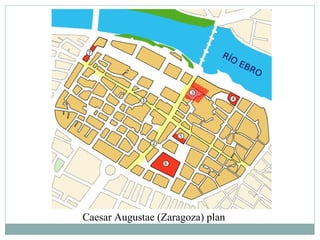
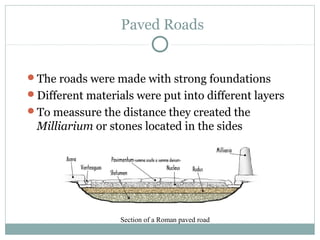
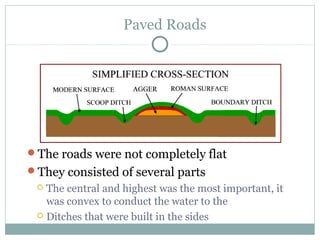
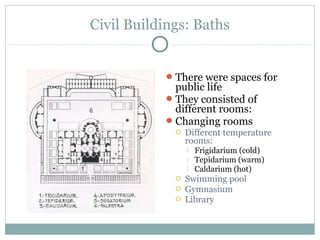
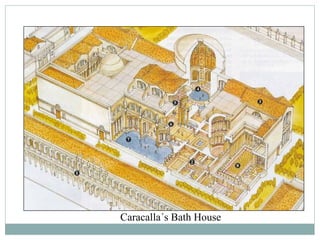
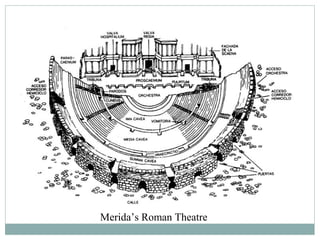
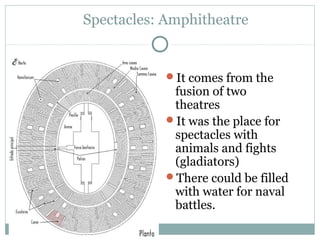
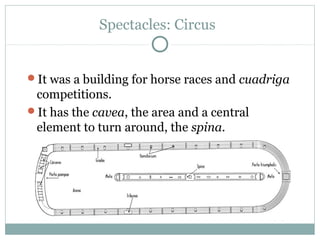
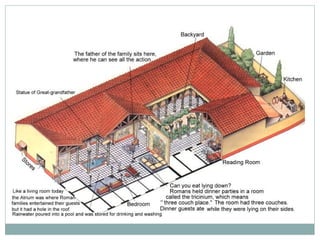
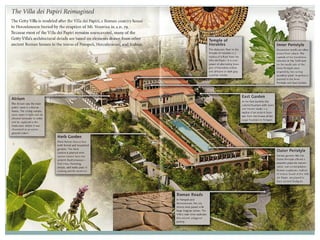
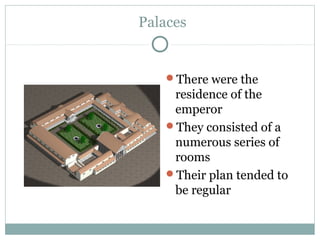
Roman architecture was influenced by earlier Italian, Etruscan, and Greek cultures. It was practical and utilitarian, emphasizing public works, monumentality, and technical advances to showcase Roman power. Some key characteristics included an emphasis on interior space, combining beauty with utility, and integrating buildings into the urban landscape. Common building materials included stone, concrete, and brick in various construction techniques. Roman towns were planned around cardo and decumanus streets, with forums and infrastructure like aqueducts and roads supporting communities across the empire. Architectural styles included temples, basilicas, baths, theaters, amphitheaters, and domestic structures ranging from insulae to villas.