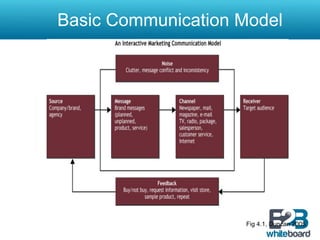
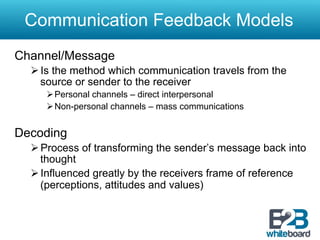
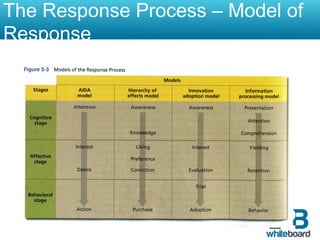
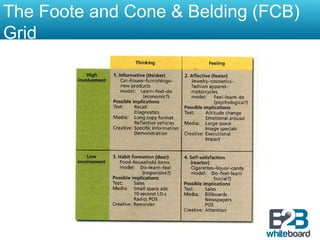
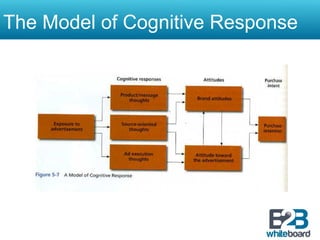
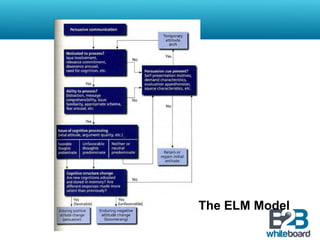
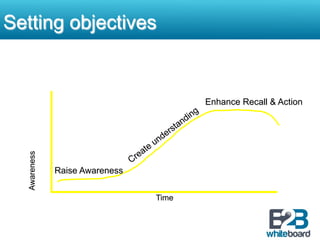
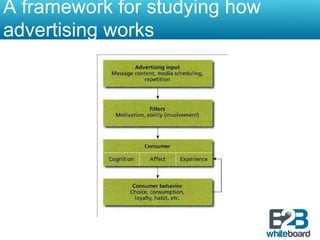
This document discusses marketing communication processes and models. It defines communication and outlines basic communication models including the source, encoding, channel, decoding, receiver, noise, and feedback. Response models are also examined, including levels of audience aggregation and the response process model. Models for evaluating responses are described, such as the FCB planning model, cognitive response approach, and elaboration likelihood model. The value of setting objectives is explained and examples of marketing versus communication objectives are provided. Frameworks for studying how advertising works and setting objectives are also outlined.