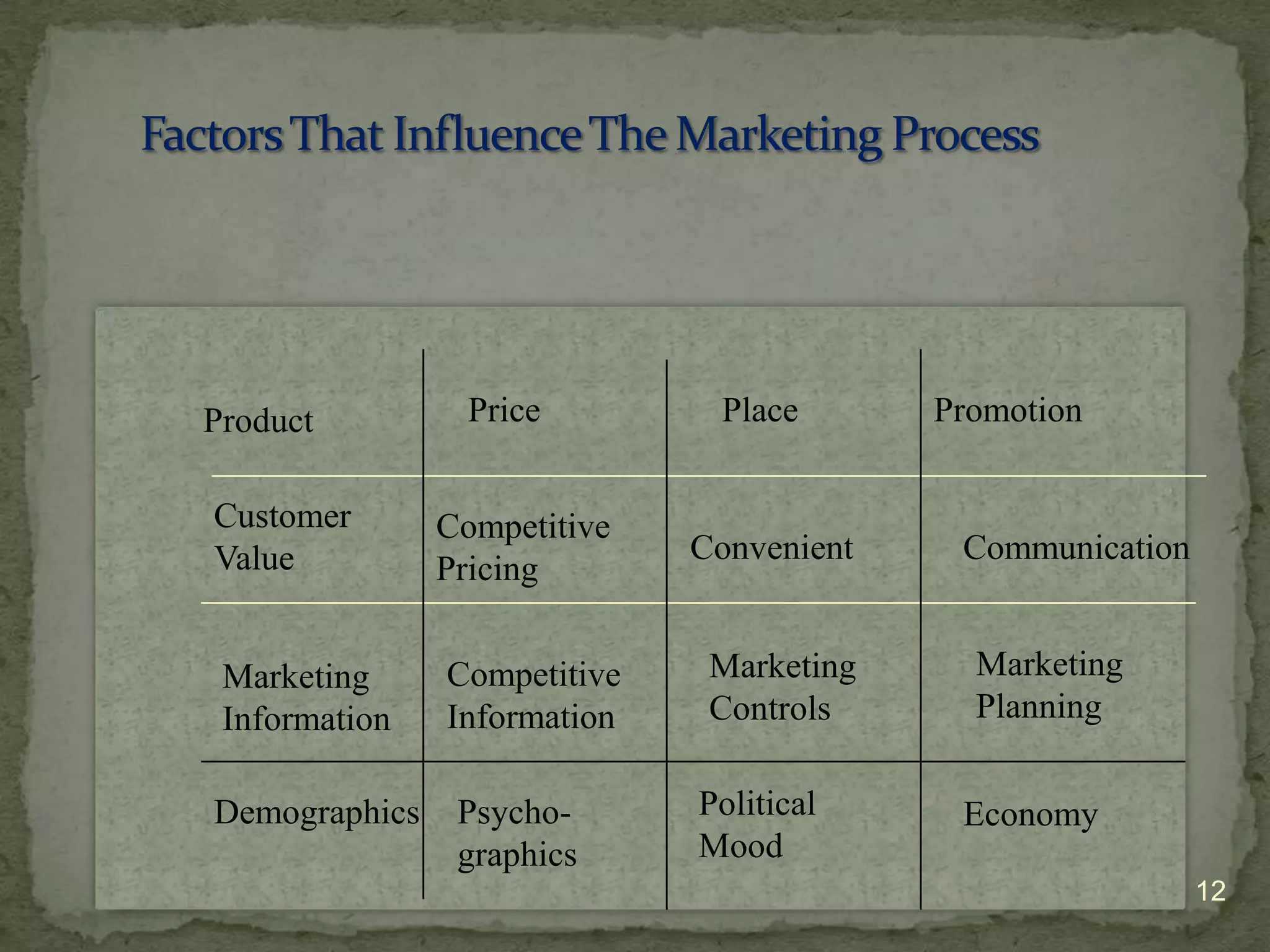
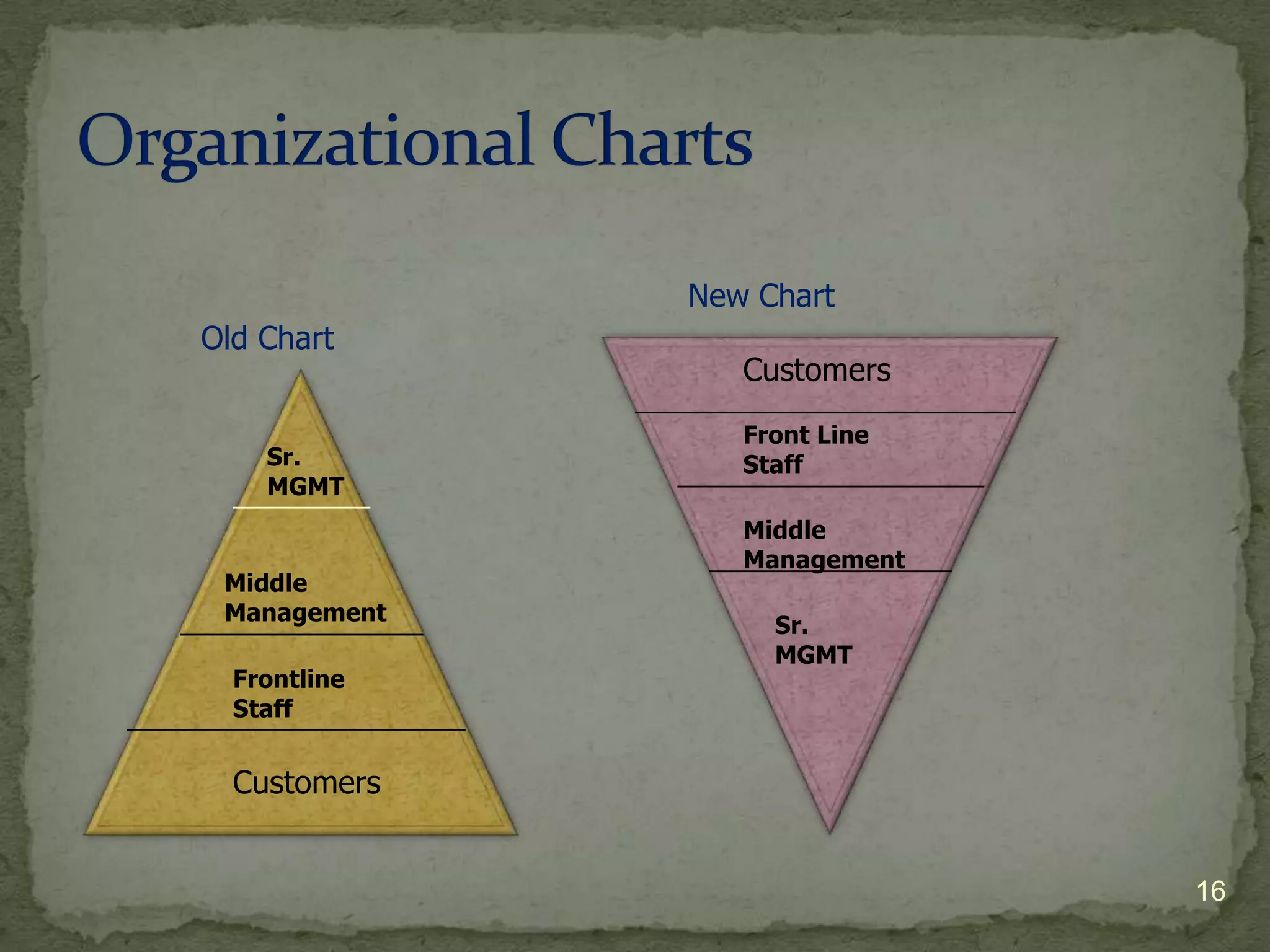
The document provides information about a marketing, advertising, and sales promotions course for entrepreneurial businesses. The course will be held on Monday evenings from 6:30 PM to 9:30 PM from September 20 to December 6, 2010 in room 1209A of Bunche Hall. The course will be taught by David Novak of Tradewind Marketing and will cover various topics related to selecting target markets, differentiating products/services, pricing strategies, building and maintaining customer loyalty, and more.