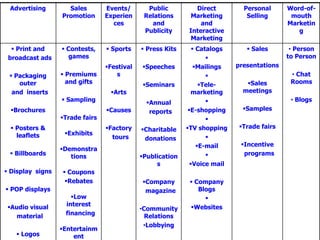
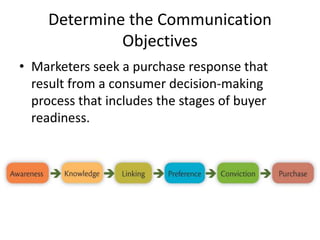
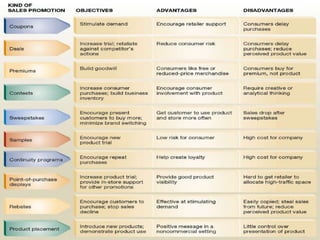
The document discusses various marketing communication tools used by firms, including advertising, sales promotion, public relations, direct marketing, and personal selling. It provides details on each tool's objectives, strategies for implementation, and factors to consider when developing an integrated marketing communications plan. The goal of marketing communications is to inform, persuade, and remind consumers about a company's products and brands through an optimal mix of communication channels.