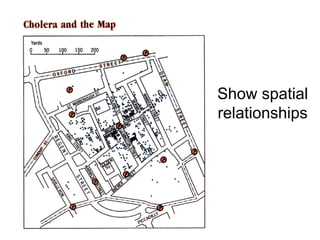
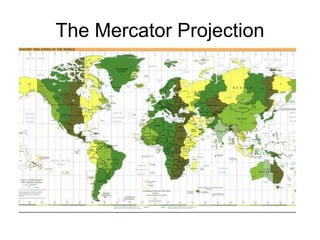
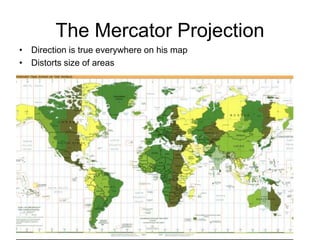
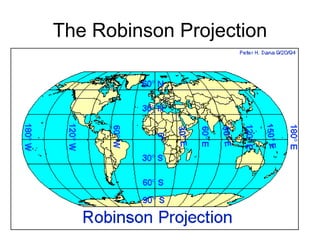
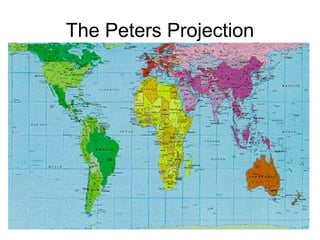
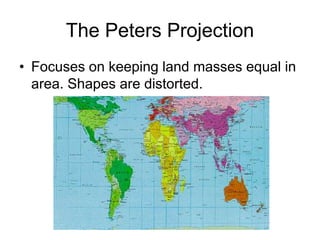
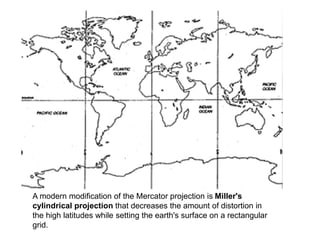
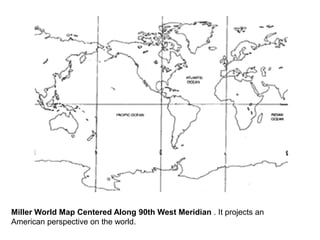
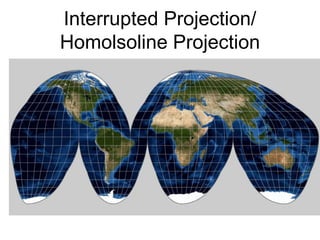
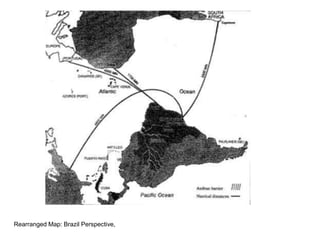
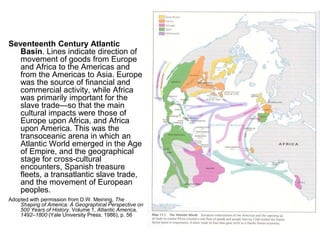
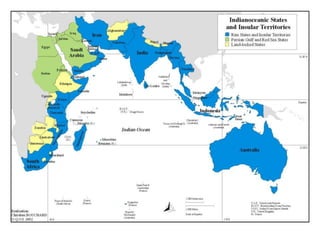
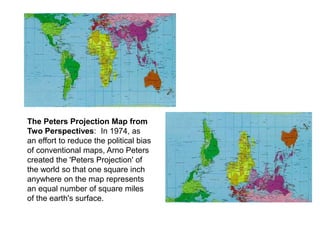
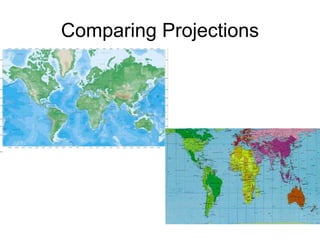
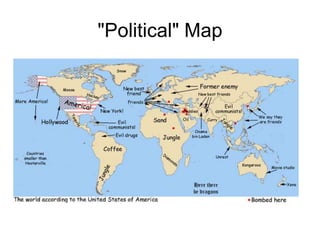
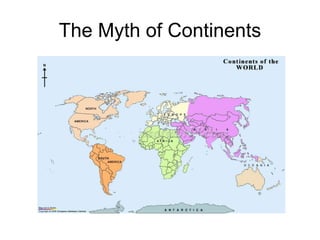
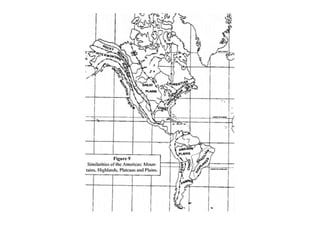
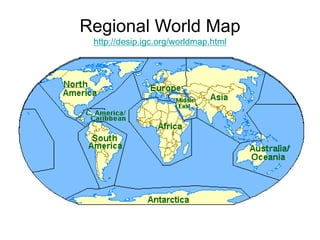
The document discusses map projections and their impact on historical perceptions, emphasizing the purpose of maps as simplified representations of the earth. It highlights various map projections such as Mercator, Robinson, and Peters, each with distinct advantages and distortions. Additionally, the document questions traditional continental divisions, advocating for a regional classification that better reflects cultural and historical realities.