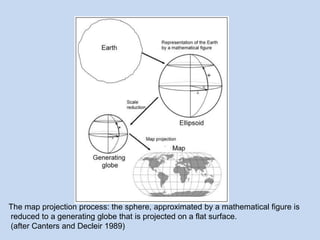
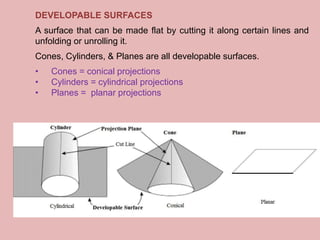
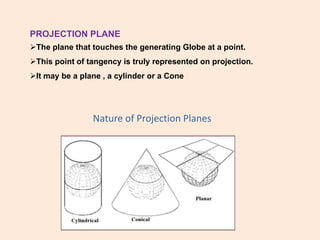
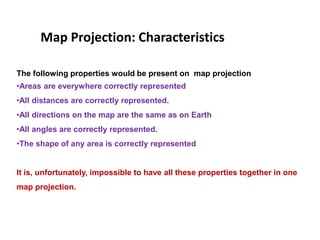
This document defines map projections and their basic concepts. It discusses that map projections are a means of depicting the earth's spherical surface on a flat plane. The key aspects covered are:
- Map projections transform the 3D globe onto a 2D surface through a process of generating a globe and projecting it onto a plane.
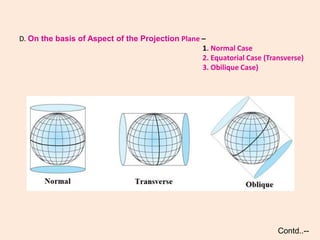
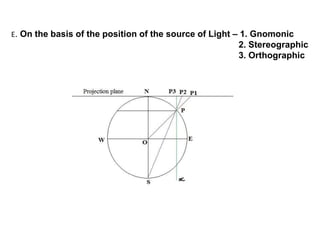
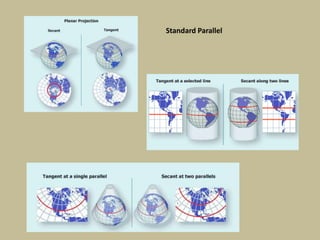
- The projection plane can be planar, cylindrical, or conical based on the surface used. Different properties are maintained based on the type of projection.
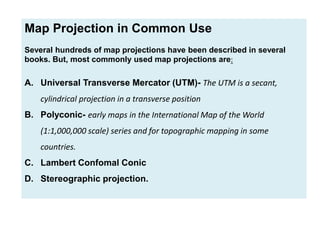
- Common map projections in use include the Universal Transverse Mercator, Polyconic, Lambert Conformal Conic, and Stereographic projections.