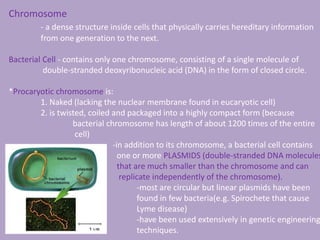
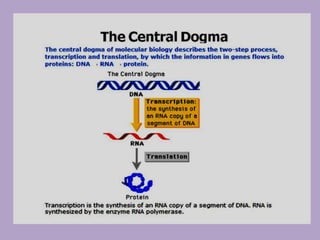
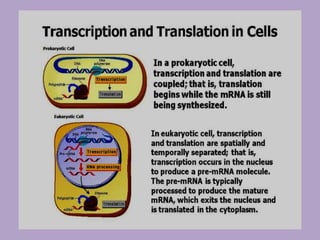
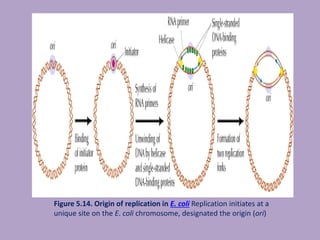
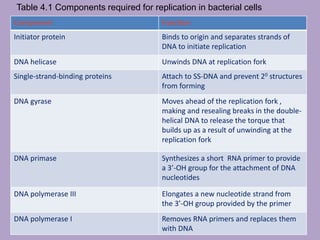
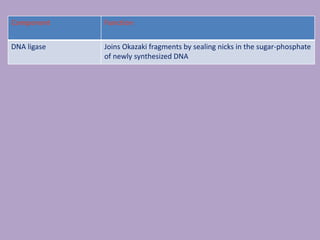
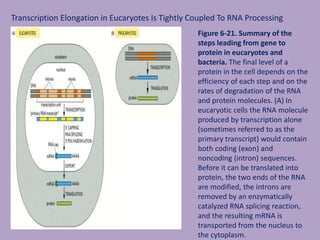
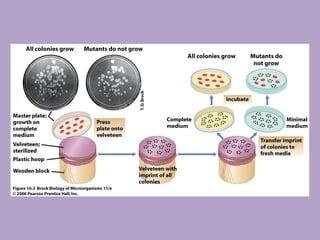
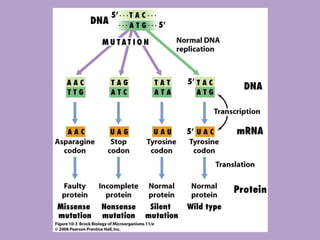
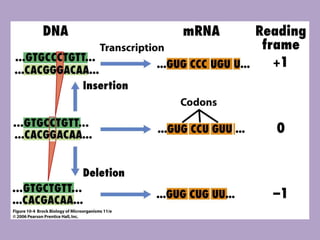
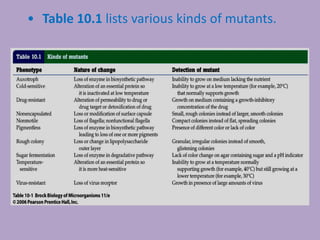
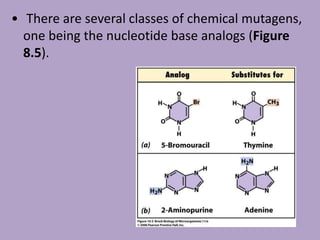
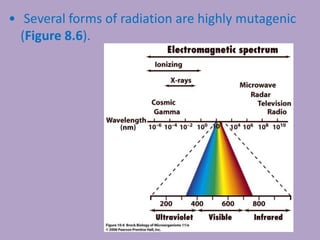
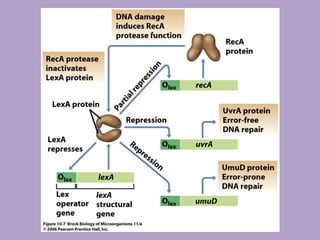
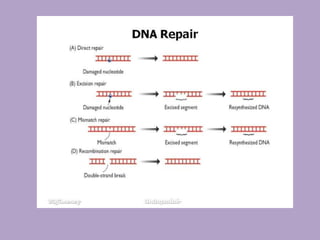
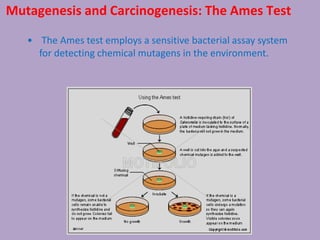
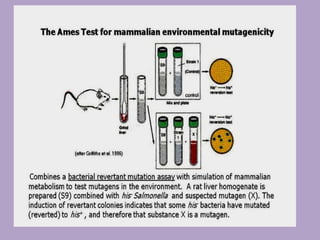
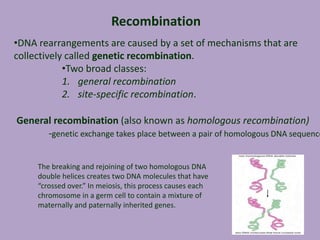
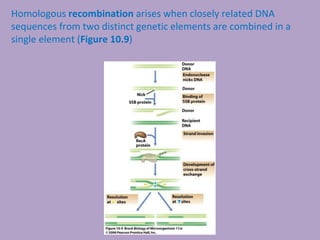
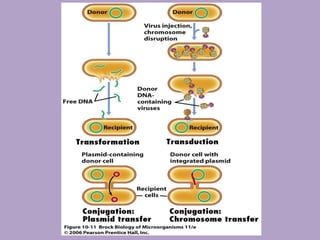
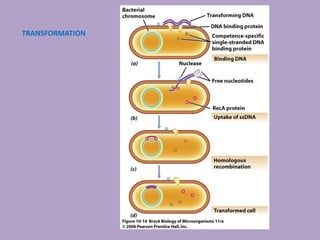
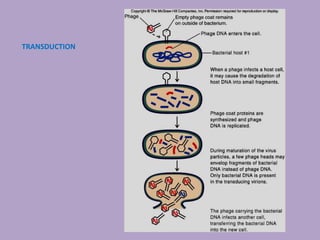
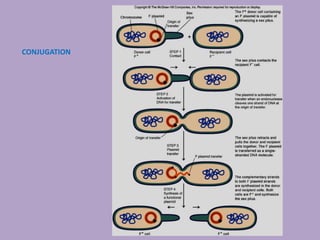
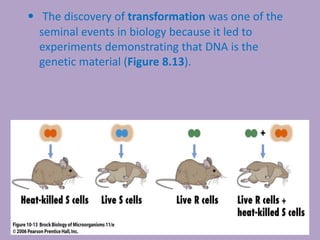
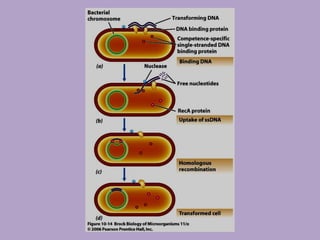
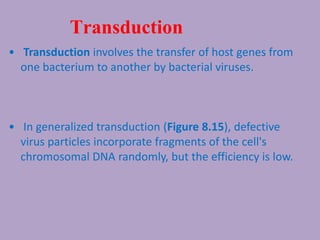
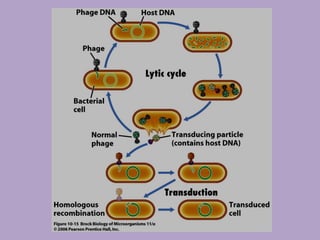
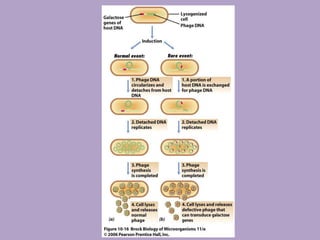
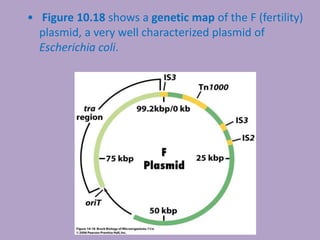
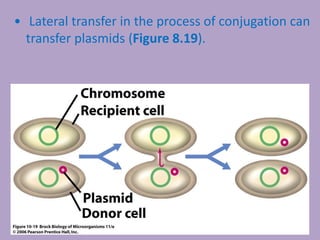
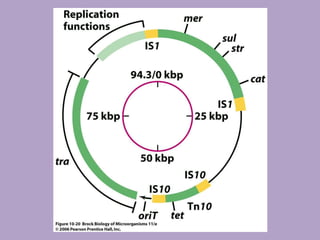
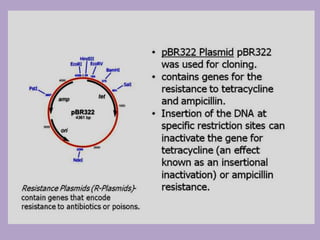
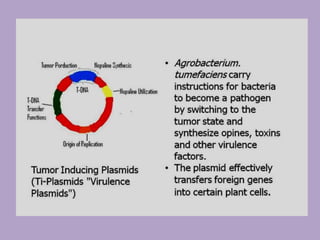
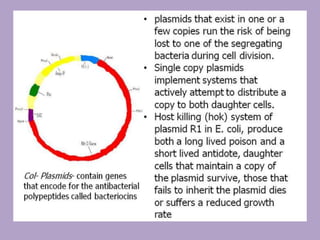
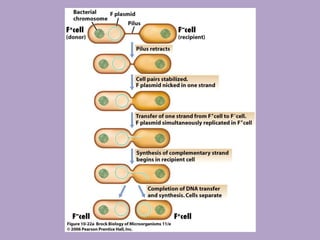
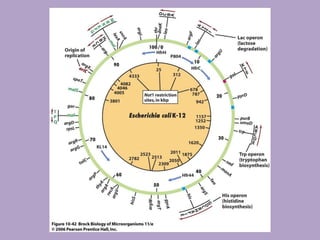
Microbial genetics involves the transmission of hereditary traits in microorganisms. It plays a role in developing fields like molecular and cell biology. Bacteria contain a single circular chromosome made of DNA that is compacted. Bacteria can also contain plasmids. DNA replication copies the parental DNA. Variability in microorganisms comes from changes in genotype and phenotype from factors like mutation and recombination. Mutation rates depend on type and can be increased by mutagens. Recombination involves processes like transformation, transduction, and conjugation. Plasmids can confer traits like antibiotic resistance and are transferred by conjugation. Gene expression in bacteria is regulated through mechanisms like induction and repression that control operons.