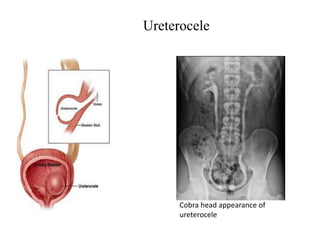
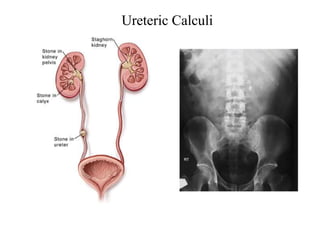
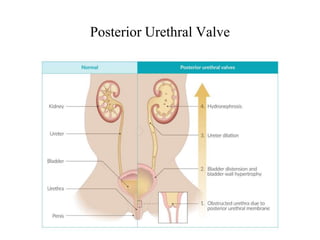
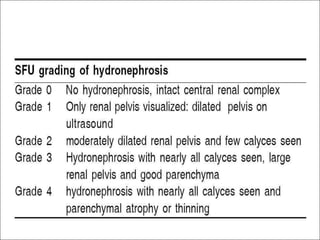
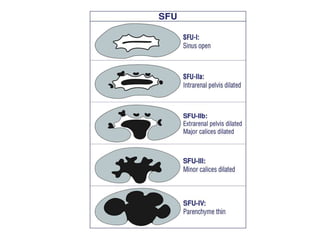
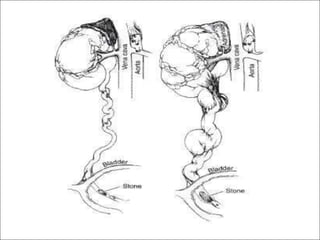
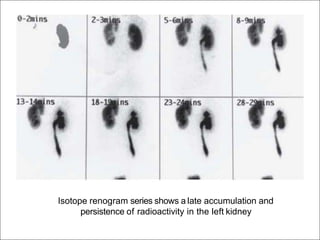
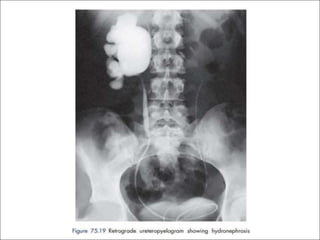
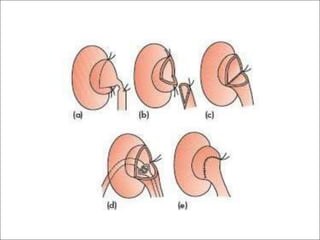
Hydronephrosis is dilatation of the kidney caused by urine outflow obstruction anywhere along the urinary tract. It can be caused by extramural factors like tumors or retroperitoneal fibrosis, or intramural factors like congenital abnormalities or inflammatory strictures. Bilateral hydronephrosis is commonly due to urethral obstruction from conditions like benign prostatic enlargement. Clinical features depend on severity and location of obstruction, and may include flank pain, urinary symptoms, or renal failure. Diagnosis involves imaging tests like ultrasound and IVU. Treatment involves relieving obstruction through stents, nephrostomy, or open surgery like pyeloplasty depending on severity and cause of obstruction.