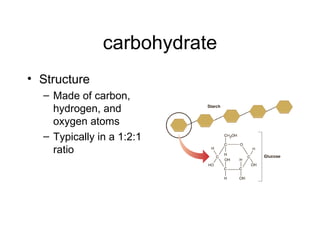
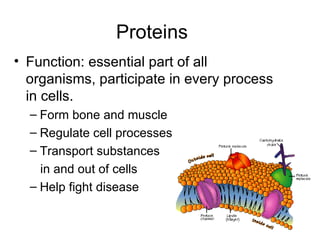
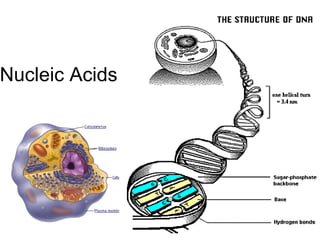
The document provides information about the four main types of macromolecules - carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It defines each macromolecule and discusses their monomer units, polymeric structures, functions in living things, and important examples. Key details provided include that carbohydrates function as an energy source, lipids function in energy storage and insulation, proteins are essential to all organisms and participate in all cell processes, and nucleic acids function to store and transmit genetic information.