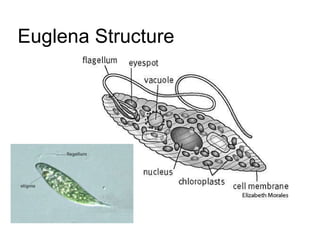
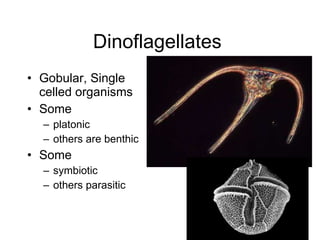
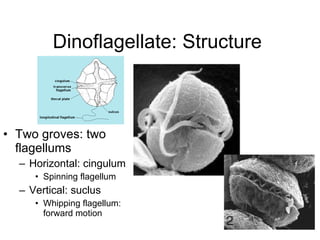
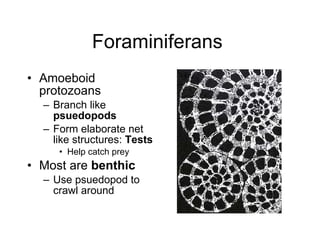
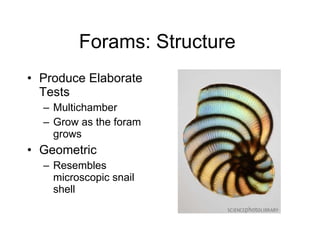
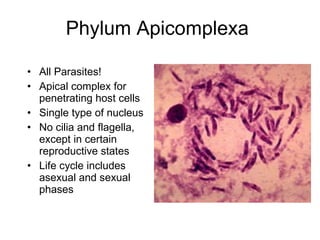
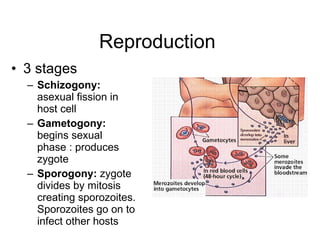
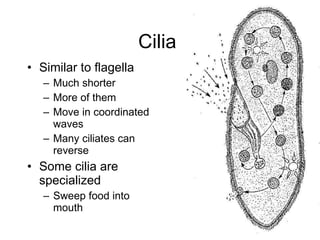
The document discusses several types of protozoa and protists, including those that are animal-like. It describes the characteristics of phyla Sarcomastigophora, Apicomplexa, and Ciliophora. Many protozoa are unicellular but have complex behaviors and life cycles. They can be photosynthetic, parasitic, or form symbiotic relationships with other organisms. Reproduction may involve asexual or sexual phases through binary fission or sporogony.