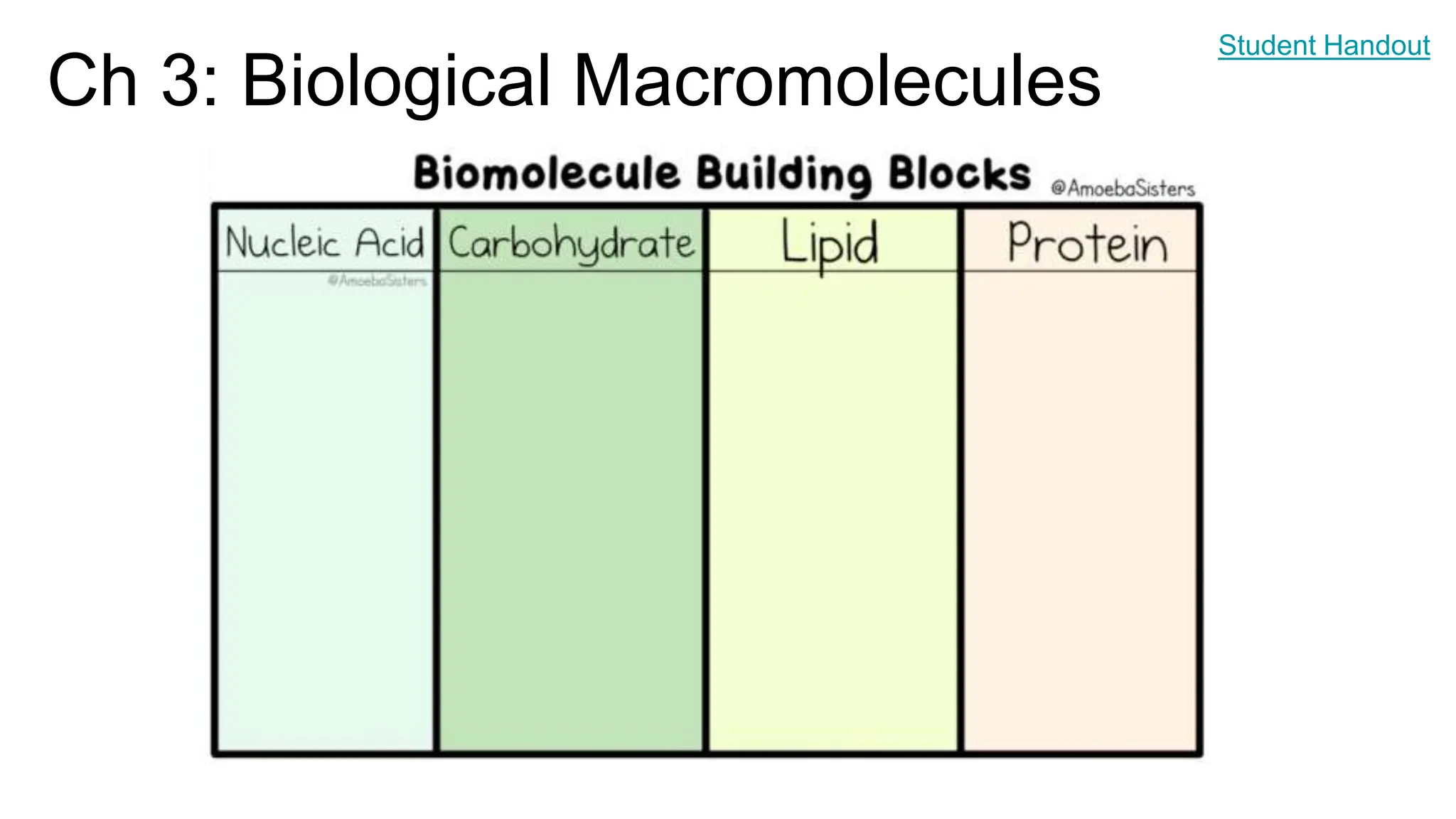
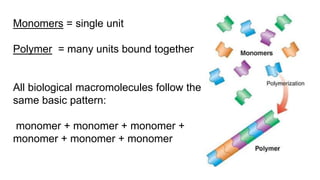
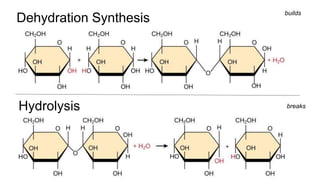
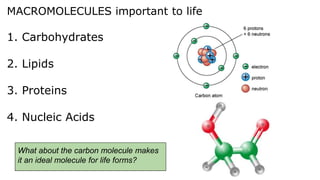
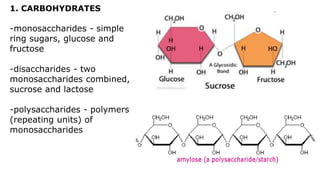
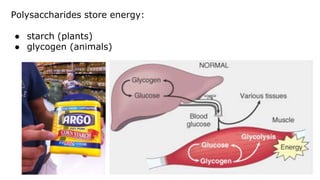
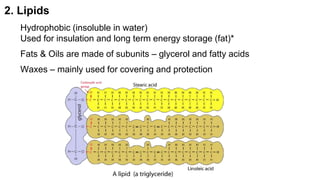
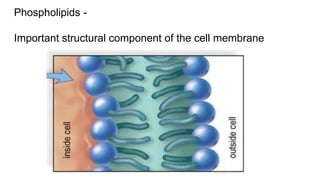
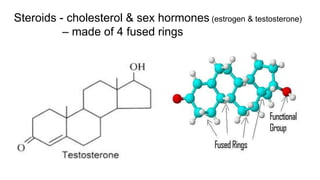
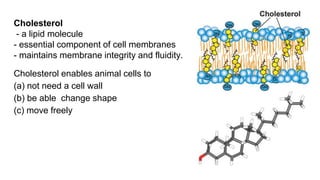
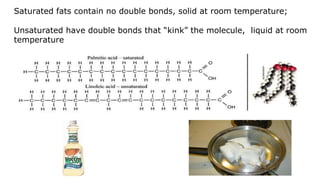
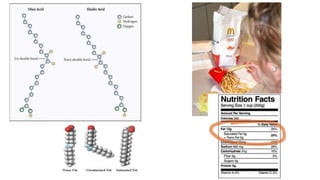
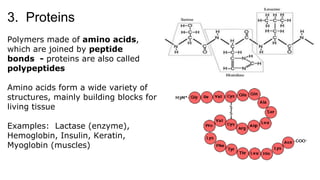
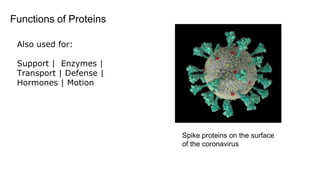
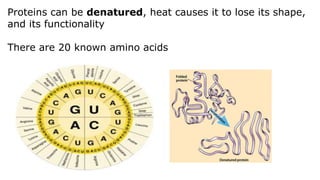
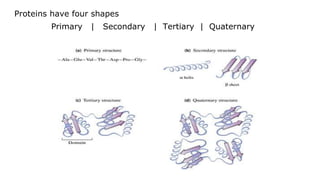
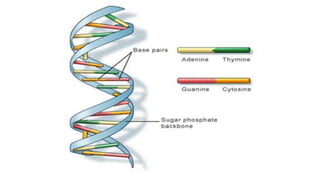
This document provides an overview of biological macromolecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It explains that monomers combine through dehydration synthesis to form polymers. Carbohydrates include monosaccharides (glucose, fructose), disaccharides (sucrose, lactose), and polysaccharides (starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin). Lipids are hydrophobic and used for insulation and energy storage, with examples being fats, oils, phospholipids, and steroids like cholesterol. Proteins are made of amino acids joined by peptide bonds and perform important structural and functional roles. Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA contain nucleotides of sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen bases and