Embed presentation
Downloaded 1,810 times

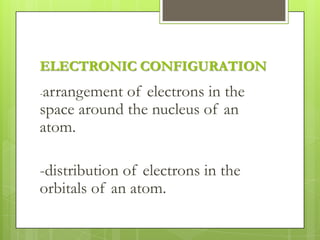









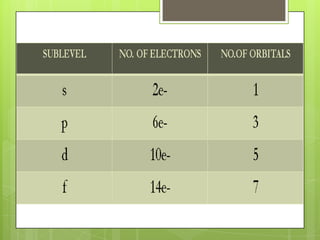




The document discusses the electronic configuration of atoms, which is the arrangement of electrons in an atom's orbitals. It defines the key terms of energy levels and sublevels, which are the orbitals where electrons are arranged. Examples of electronic configurations are given for several elements, such as iodine and silicon. Rules for determining electronic configuration, such as Aufbau's principle, Pauli's exclusion principle, and Hund's rule are also outlined.














