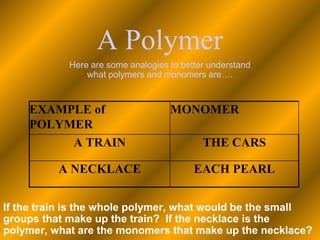
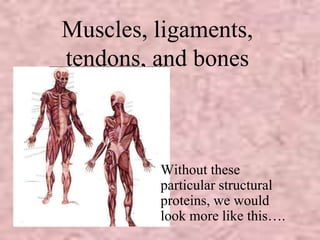
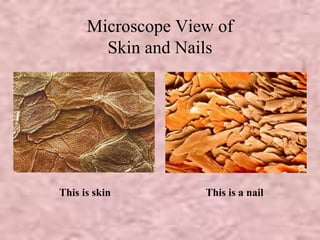
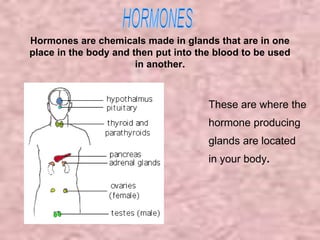
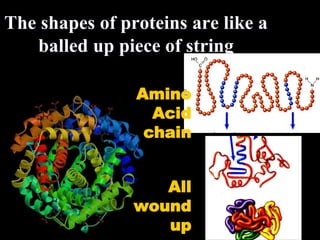
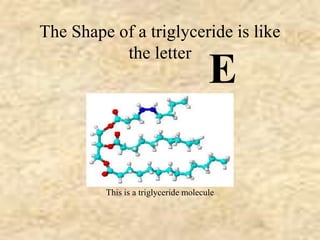
The document discusses the four classes of biological macromolecules: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. It provides details about each macromolecule, including their monomers, polymers, structure, functions in the body, and examples of where they can be found. Carbohydrates are made of monomers of glucose and provide energy. Proteins are made of amino acid monomers and are involved in structure, enzymes, and hormones. Lipids are made of glycerol and fatty acid monomers and function in energy storage, insulation, and hormones.