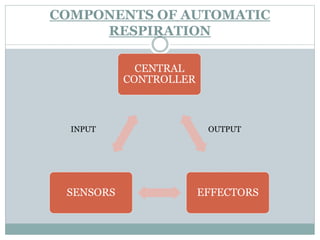
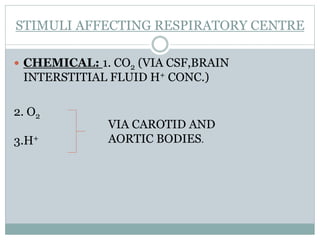
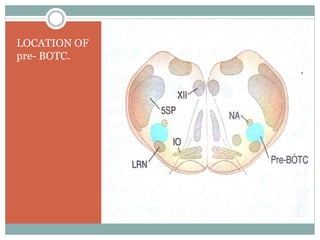
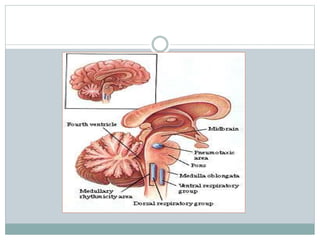
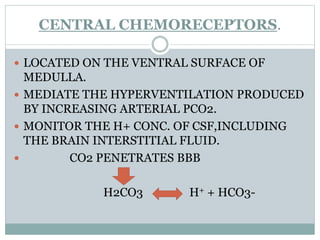
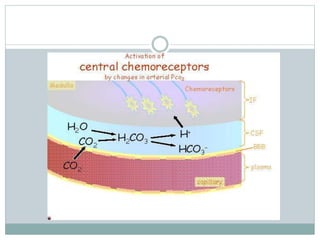
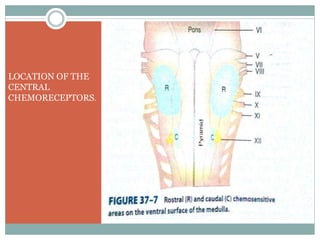
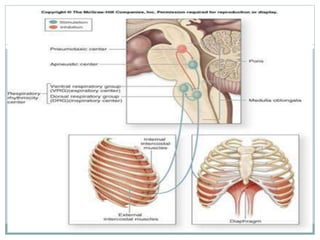
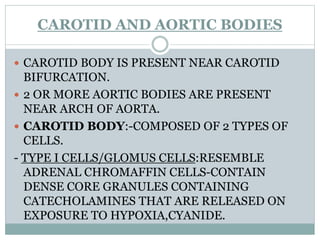
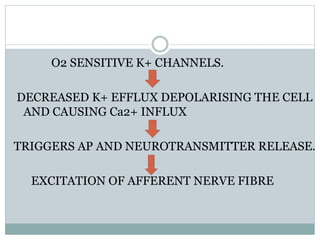
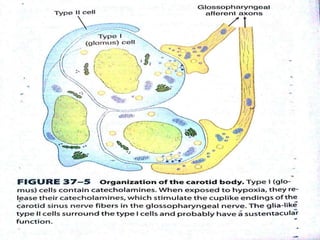
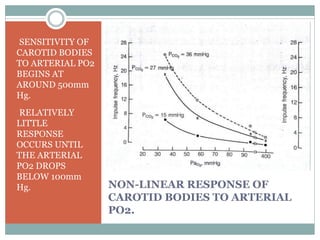
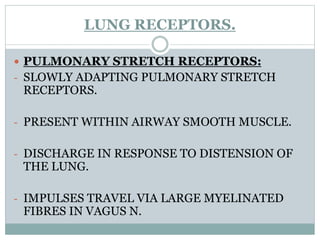
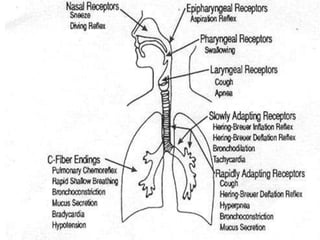
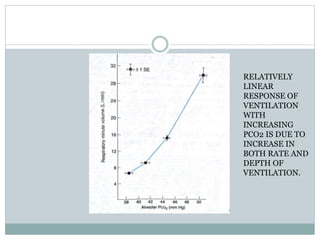
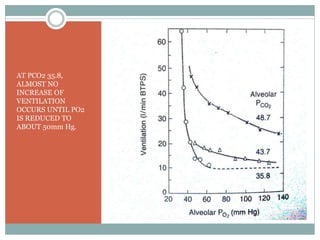
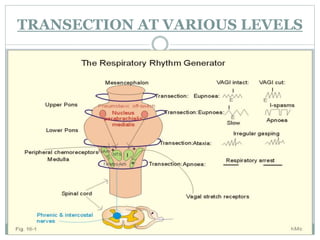
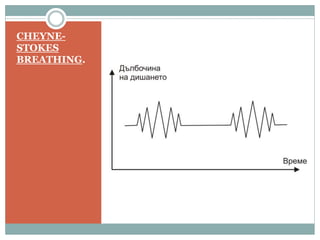
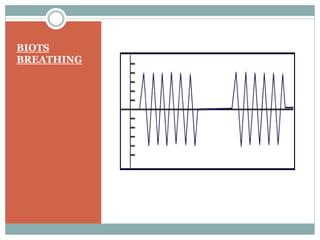
This document discusses the control of breathing and the neural mechanisms that regulate respiration. There are two main mechanisms - voluntary control located in the cerebral cortex, and automatic control driven by pacemaker cells in the medulla. The medulla contains respiratory centers that generate the rhythmic pattern of breathing through inspiratory and expiratory motor neurons. Breathing is regulated by chemical and non-chemical stimuli that act on central and peripheral chemoreceptors to modulate the respiratory centers. Abnormalities in the respiratory rhythm can occur due to lesions or diseases that disrupt the control centers.