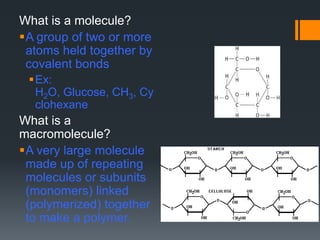
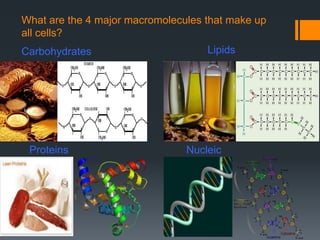
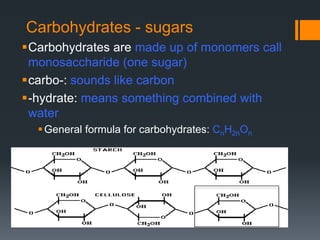
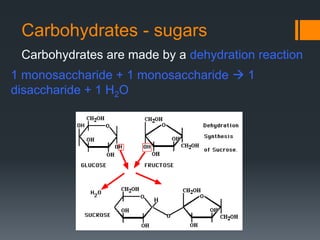
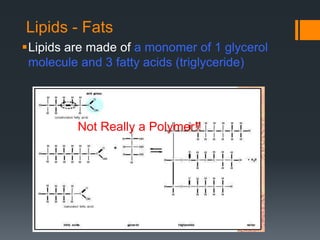
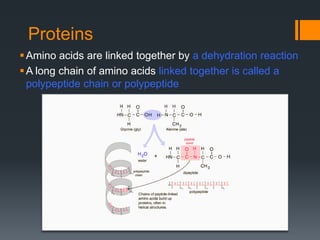
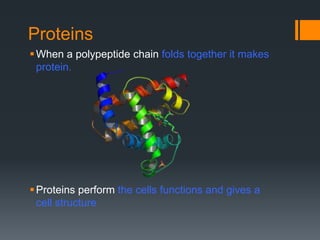
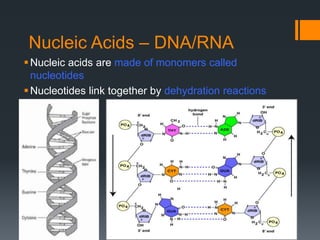
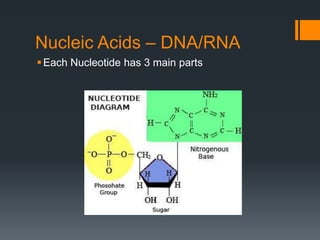
Macromolecules are large molecules composed of repeating subunits called monomers. There are four main types of macromolecules that make up cells: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates are made of monosaccharides linked together and function as an energy source. Lipids are made of glycerol and fatty acids and serve as an energy store. Proteins are composed of amino acids linked in chains that fold into shapes to perform the cell's functions. Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA are made of nucleotides linked together to store and transmit genetic information.