Embed presentation
Download to read offline




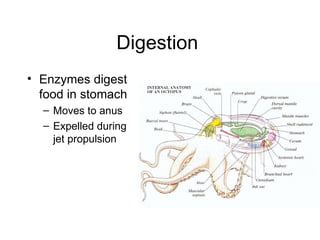



Cephalopods such as octopus, squid, and cuttlefish are fierce predators with large brains, complex sensory structures, and rapid locomotion enabled by jet propulsion. They have advanced eyes similar to vertebrates and can change their skin color rapidly using specialized cells. Their highly developed nervous systems and grasping tentacles allow them to both hunt prey and defend themselves as skilled predators in the ocean.







