Embed presentation
Downloaded 60 times

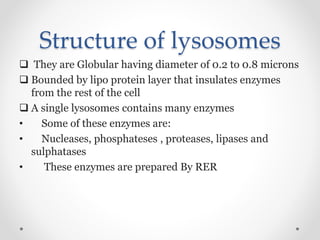

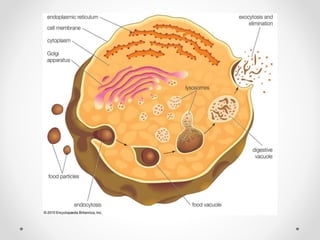
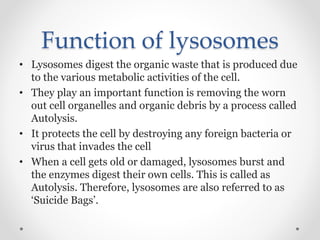


Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes and are capable of breaking down most biological molecules. They are spherical, bounded by a single membrane, and range in size from 0.2 to 0.8 microns. Lysosomes contain many enzymes that are produced by the rough endoplasmic reticulum and help the cell digest waste, remove old or damaged cell components through autolysis, and destroy any invading bacteria or viruses.






