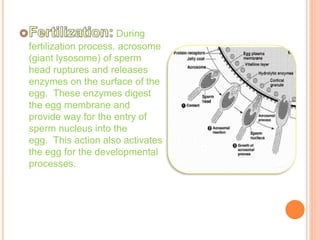
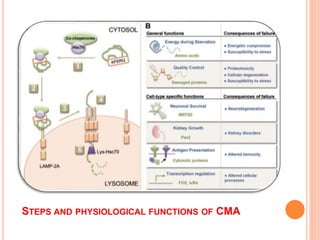
This document discusses lysosomes and chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA). It provides background on the discovery of lysosomes and their structure and functions. Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes and digest macromolecules, cellular debris, and foreign material. CMA selectively degrades cytosolic proteins through binding to a chaperone and lysosomal membrane protein LAMP-2A. Disruption of CMA is implicated in diseases like Parkinson's and cancer. CMA activity declines with age.