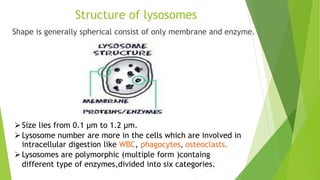
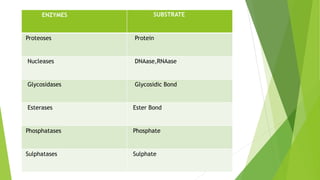
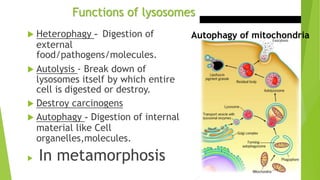
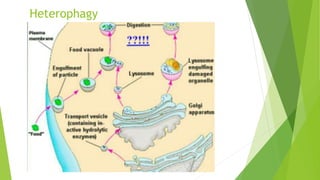
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles containing enzymes to break down biological polymers, discovered by Christian de Duve. They have varied forms including primary, secondary, and tertiary lysosomes, each with distinct functions related to digestion and cell maintenance. Key roles include heterophagy, autolysis, and autophagy, essential for cellular processes in eukaryotic organisms.