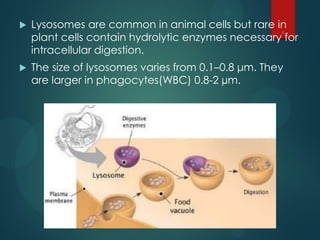
Lysosomes are spherical organelles that contain digestive enzymes called hydrolases. They are produced in the Golgi apparatus and contain hydrolytic enzymes that help break down macromolecules through processes like phagocytosis, endocytosis, and autophagy. Lysosomes function to digest cellular waste and debris and are sometimes referred to as the cell's "garbage disposal" or "recycling unit." Diseases can occur if lysosomal enzymes do not function properly or reach the lysosome, preventing the breakdown of cellular components and leading to their accumulation.