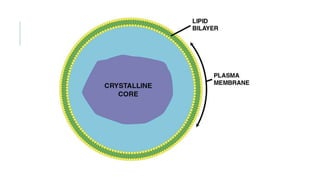
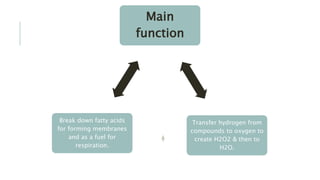
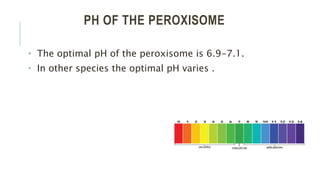
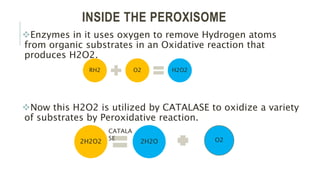
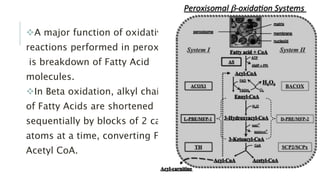
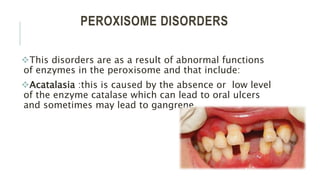
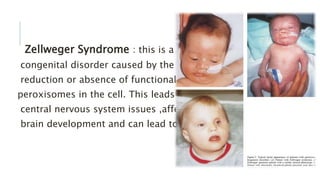
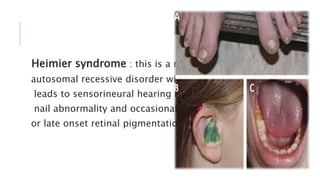
Peroxisomes are single-membrane organelles found in the cytoplasm of human cells that contain enzymes for oxidizing molecules like fatty acids. They are 0.1-1 micrometers in diameter and cells contain up to 100 peroxisomes. Peroxisomes are formed through self-replication since they lack DNA and ribosomes. Their functions include producing hydrogen peroxide during fatty acid breakdown, synthesizing phospholipids and bile acids, and detoxifying alcohol. Disorders can occur if peroxisomal enzymes are absent or nonfunctional, leading to issues like oral ulcers, impaired brain development, or hearing loss.