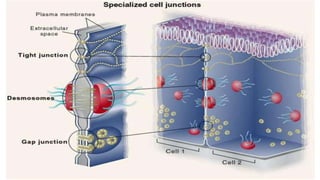
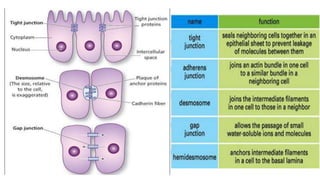
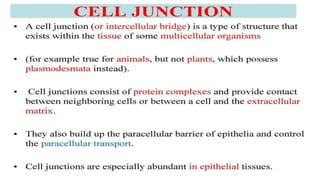
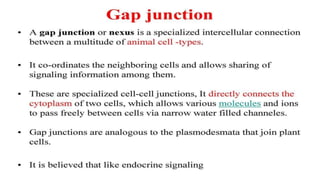
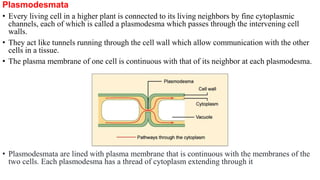
Plasmodesmata are cytoplasmic channels that connect plant cells and allow communication between them. They form during cell division around elements of the endoplasmic reticulum that become trapped in the cell wall. Plasmodesmata vary in structure and number, ranging from less than 1 to over 15 per square micrometer of cell wall. They function to transport molecules, nutrients, and signals between cells, facilitating intercellular communication and transport throughout plant tissues.