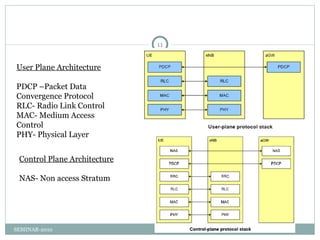
The document summarizes Long Term Evolution (LTE) technology. It discusses the evolution of LTE from 3G networks and its key features like downlink speeds of 100Mbps. The technologies that LTE uses are described, including OFDMA for downlink and SC-FDMA for uplink. LTE architecture is explained as a flat all-IP architecture with E-UTRAN and EPC components. Future applications of LTE Advanced and 4G are also mentioned.












![REFERENCES
14
[1.]David Astély, Erik Dahlman, Anders Furuskär, Ylva Jading,
Magnus Lindström, and Stefan Parkvall, LTE: The Evolution of
Mobile Broadband, IEEE Communications Magazine, April
2009, Vol. 47, no. 4, pp. 44 – 51.
[2.] Mamoru Sawahashi, Yoshihisa Kishiyama, Hidekazu Taoka,
Motohiro Tanno, and Takehiro Nakamura, Broadband Radio
Access: LTE and LTE-Advanced, International Symposium on
Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems
(ISPACS 2009), Dec. 2009, pp. 224-227.
[3.] www.3gpp.org/lte (accessed on 12/08/2010)
[4.] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3GPP_Long_Term_Evolution
(accessed on 12/08/2010)
SEMINAR-2010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/longtermevolution-120625021051-phpapp01/85/Long-term-evolution-14-320.jpg)
