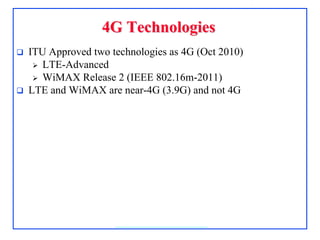
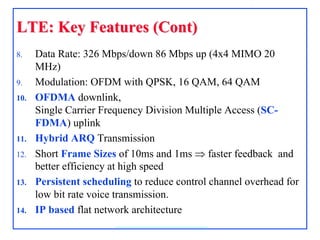
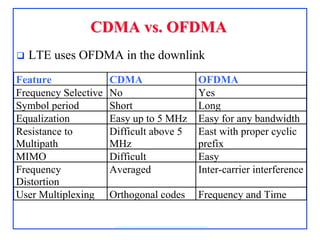
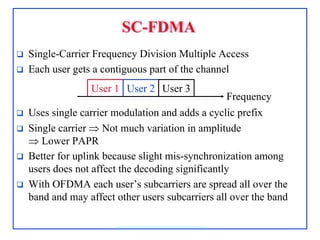
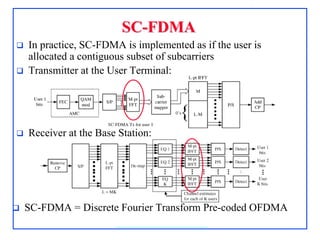
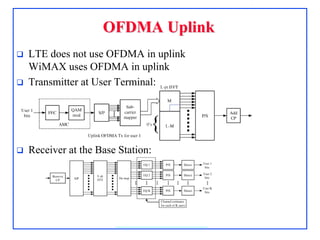
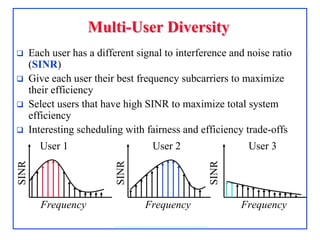
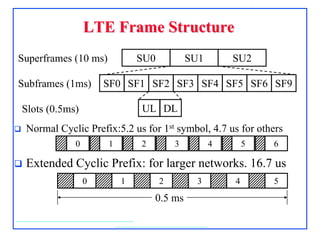
4G, defined as IMT-Advanced, demands peak rates of 1 Gbps for fixed and 100 Mbps for mobile services, utilizing technologies like LTE-Advanced and WiMAX. Key features include flexible bandwidth, high mobility, and advanced signaling techniques such as SC-FDMA for uplink, which differentiates it from CDMA. The LTE protocol stack supports efficient data transmission through various layers, ensuring optimized performance and seamless user experiences.