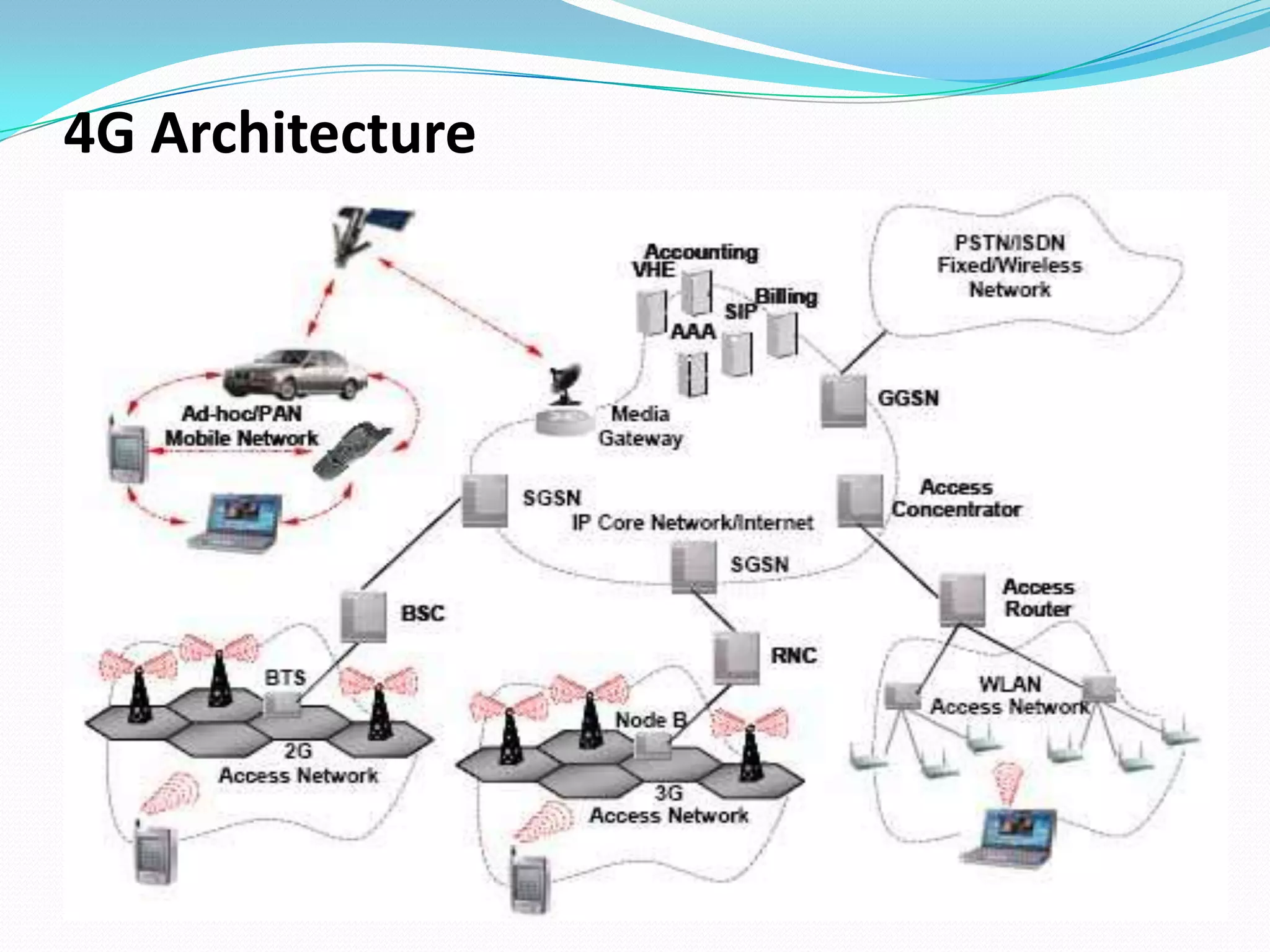
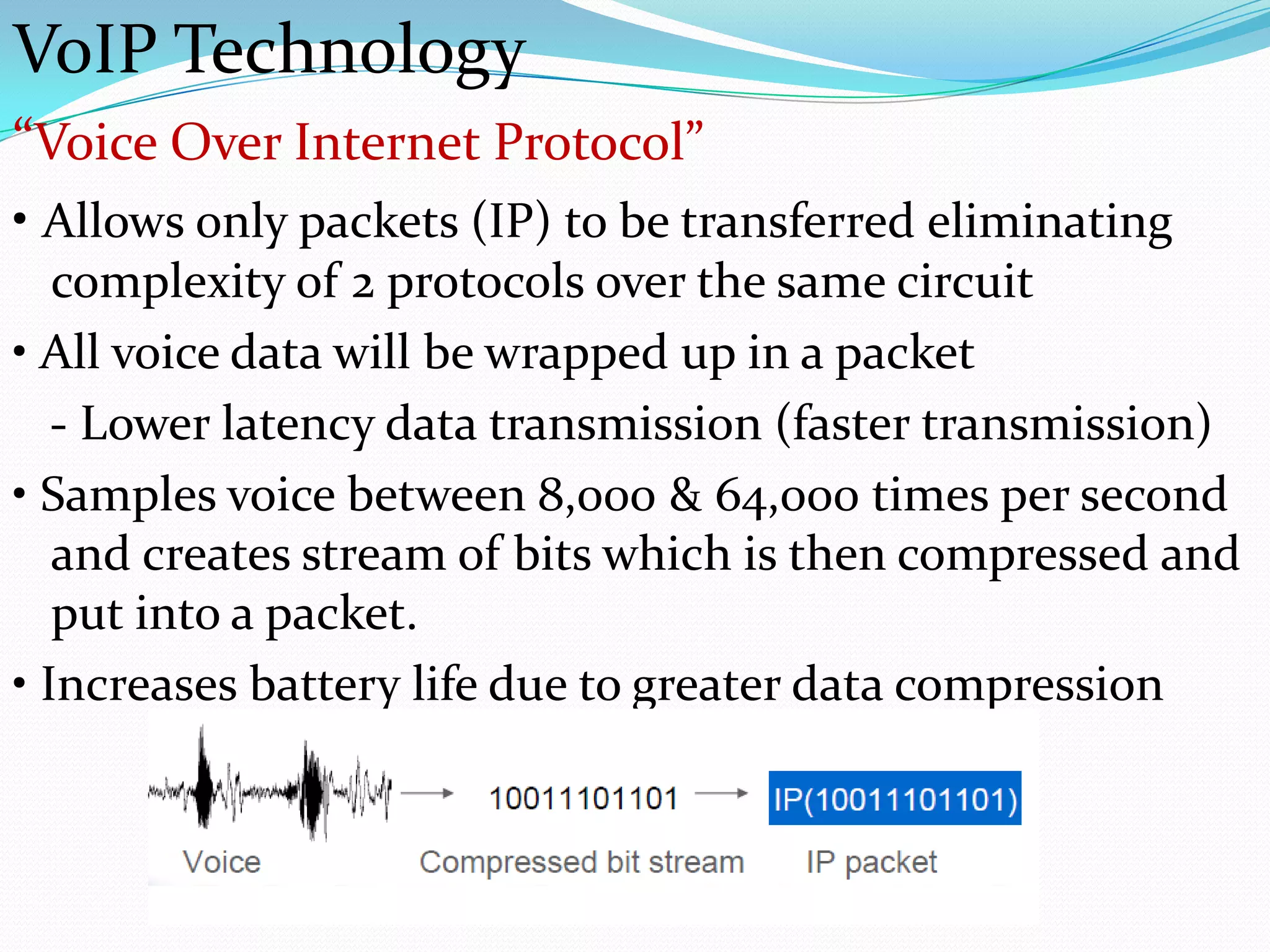
This document summarizes a presentation on 4G technology. It begins by outlining earlier wireless technologies like 1G, 2G, and 3G. It then defines 4G as characterized by high-speed data rates up to 100 Mbps for mobile users and 1 Gbps for stationary users. Key technologies that enable 4G are described like MIMO antennas, IPv6, VoIP, OFDM, and software-defined radio. Applications and advantages of 4G include support for multimedia, global access, and improved spectral efficiency. Challenges in fully realizing 4G capabilities are also discussed.