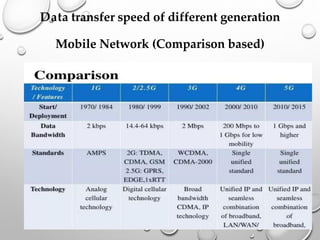
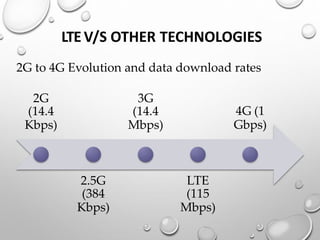
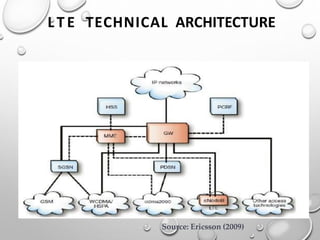
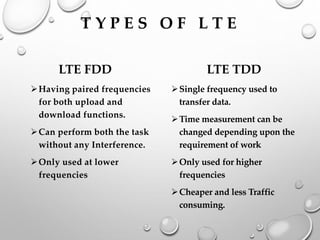
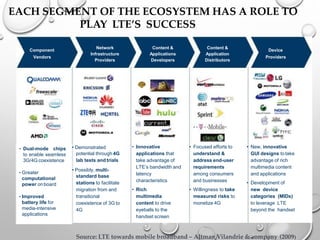
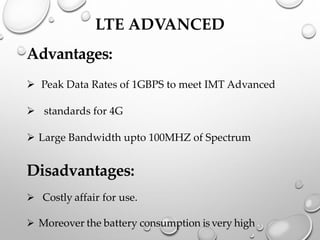
This document provides an overview of LTE (Long Term Evolution) concepts. It discusses the 4G ideal concept, defines LTE and its advantages over 3G technologies. It also describes LTE's technical architecture, types of LTE, network elements, calling procedures, potential business impacts, and future uses. LTE Advanced is introduced as an evolution of LTE to support higher peak data rates of 1Gbps. The document concludes that LTE has surpassed previous generations in mobile communication.