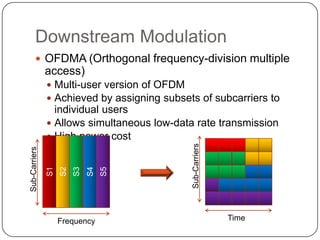
4G LTE uses technologies like OFDMA, SC-FDMA and MIMO to provide peak download rates of 100 Mbps and upload rates of 50 Mbps, with low latency. It employs an all-IP packet switched network with scalable channel bandwidth between 5-20 MHz. The LTE network architecture consists solely of evolved NodeBs which simplify the design.