LTE Advanced is a 4G mobile communication standard approved by the ITU in 2012, designed to enhance traditional LTE capabilities with features such as improved peak data rates, spectrum efficiency, and reduced latency. It utilizes advanced technologies like self-optimizing networks, carrier aggregation, and coordinated multipoint transmission. While industry trials show its viability, the actual deployment timing depends on market demand and existing LTE rollouts.

![chaitanya.singh87@gmail.com
INTRODUCTION
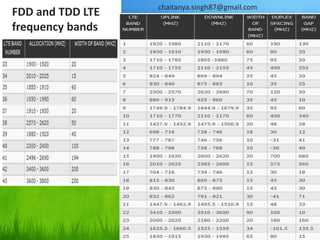
• LTE Advanced is a mobile communication 4G standard
approved by International Telecommunications Union
(ITU) in Jan 2012 [1].
• Standardized by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project
(3GPP) as a major enhancement of the Long Term
Evolution (LTE) standard.
• It incorporates many enhancements including the
aggregation of multiple radio channels, advanced
antenna techniques, advanced network topology
and others.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lteadvanced-120216004615-phpapp01/85/LTE-Advanced-The-Global-4G-Standard-2-320.jpg)
![chaitanya.singh87@gmail.com
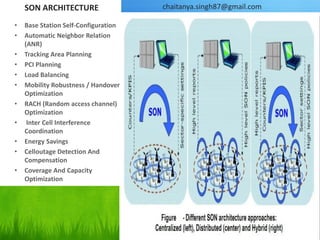
Evolutionary Trends
Source of Figure : [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lteadvanced-120216004615-phpapp01/85/LTE-Advanced-The-Global-4G-Standard-3-320.jpg)


![chaitanya.singh87@gmail.com
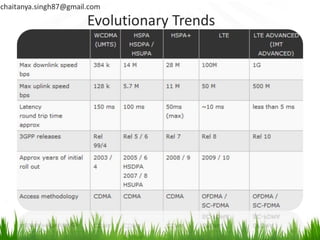
• Self-Optimizing Networks
Self configuration Self optimization Self healing
Source of Figure: [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lteadvanced-120216004615-phpapp01/85/LTE-Advanced-The-Global-4G-Standard-7-320.jpg)
![chaitanya.singh87@gmail.com
• Carrier aggregation
Source of Figure: [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lteadvanced-120216004615-phpapp01/85/LTE-Advanced-The-Global-4G-Standard-8-320.jpg)
![chaitanya.singh87@gmail.com
• Range expansion
Source of Figure: [5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lteadvanced-120216004615-phpapp01/85/LTE-Advanced-The-Global-4G-Standard-9-320.jpg)
![chaitanya.singh87@gmail.com
• Coordinated Multipoint transmission & reception
• Joint processing:
• Coordinated scheduling or beamforming:
Source of Figure: [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lteadvanced-120216004615-phpapp01/85/LTE-Advanced-The-Global-4G-Standard-10-320.jpg)
![chaitanya.singh87@gmail.com
• Relaying
Source of Figure: [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lteadvanced-120216004615-phpapp01/85/LTE-Advanced-The-Global-4G-Standard-11-320.jpg)