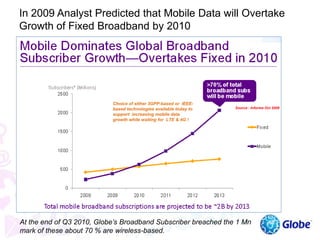
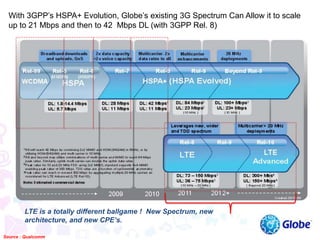
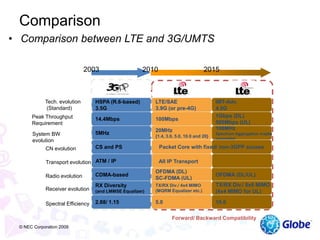
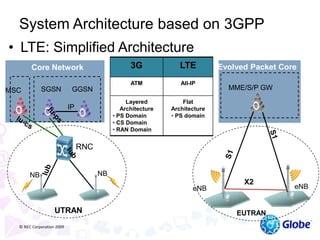
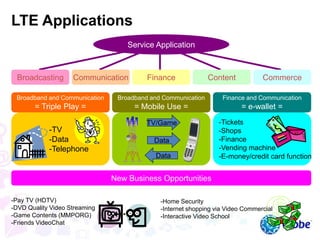
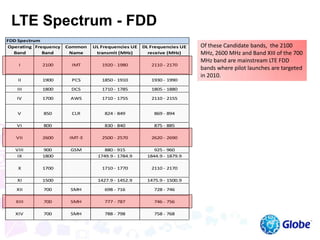
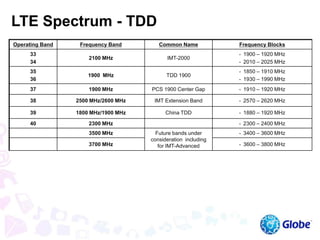
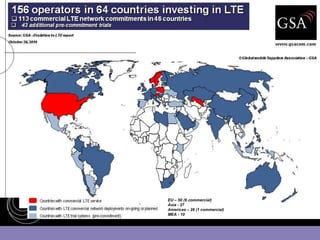
This document provides an overview of global trends in mobile data usage and LTE technology. It discusses how mobile data is overtaking fixed broadband growth. It also summarizes that LTE aims to provide improved mobile broadband through increased spectral efficiency and simplified network design. Key LTE technologies include OFDMA for downlinks and SC-FDMA for uplinks, as well as support for flexible bandwidths up to 20 MHz. The document compares LTE to 3G technologies and outlines the evolving 3GPP system architecture. Potential LTE applications and current deployment status globally are also summarized.