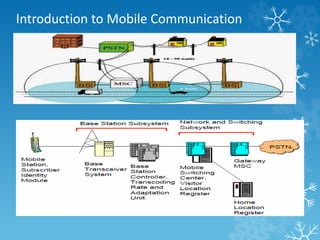
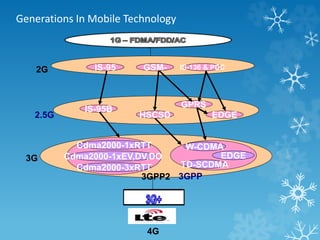
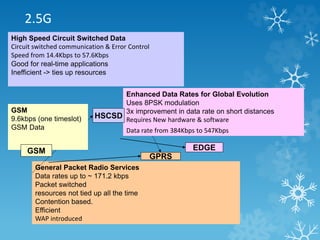
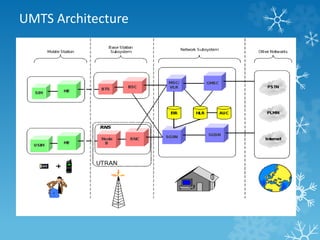
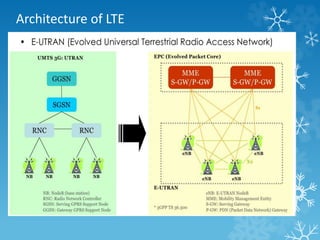
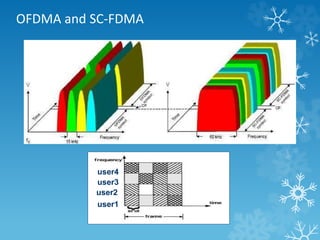
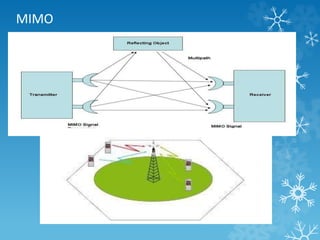
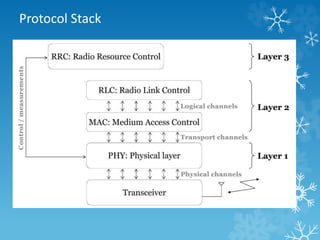
The document provides an overview of Long Term Evolution (LTE), a broadband network technology developed by 3GPP that offers data transfer rates of up to 100 Mbps. It discusses the architecture, major applications, key technologies, and market scenarios for LTE, as well as its advantages over previous mobile communication generations. The document also touches on the evolution beyond LTE, particularly LTE-Advanced, which promises higher data rates and increased efficiency.