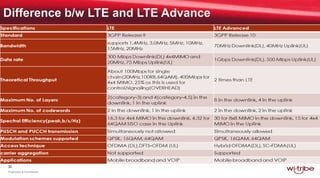
The document provides a summary of the history and evolution of internet and wireless broadband technology. It discusses the early concepts of computer networking starting in the 1960s, the development of ARPANET in the late 1960s, and the introduction of TCP/IP in the early 1970s which led to the modern internet. It then covers the emergence of dial-up internet access in the late 1970s and 1980s, and the evolution of cellular network technologies from 1G to 4G. Finally, it provides an overview of LTE and LTE-Advanced wireless broadband technologies and their capabilities.





![6
Proprietary & Confidential
Dial-up Internet access is a form of Internet access that uses the
facilities of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) to establish
a connection to an Internet service provider (ISP) by dialing
a telephone number on a conventional telephone line. The user's
computer or router uses an attached modem to encode and decode
information into and from audio frequency signals, respectively.
In 1979, Tom Truscott and Steve Bellovin, graduate students for Duke
University, would create an early predecessor to dial-up Internet
access – called the USENET. The USENET was a UNIX based
system that used a dial-up connection to transfer data through
telephone modems.[1]
Dial-up Internet has been around since the 1980s via public providers
such as NSFNET-linked universities and was first offered
commercially in July 1992 by Sprint.[2] Despite losing ground
to broadband since the late-1990s, dial-up may still be used where
other forms are not available or the cost is too high, such as in some
rural or remote areas.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lteadvancedoverview-170621170725/85/LTE-Advanced-Overview-6-320.jpg)