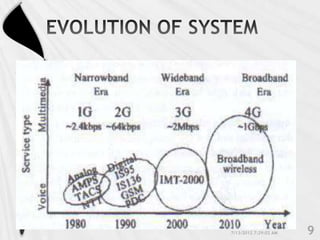
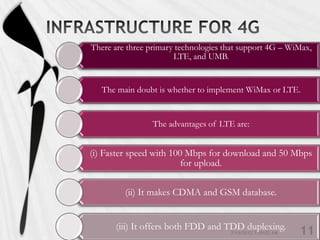
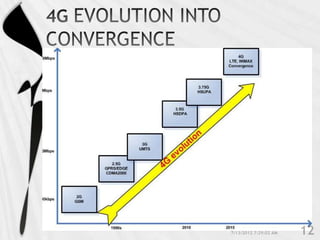
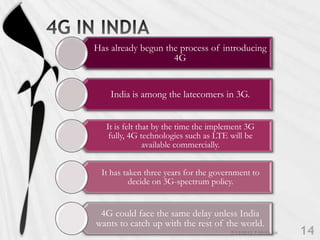
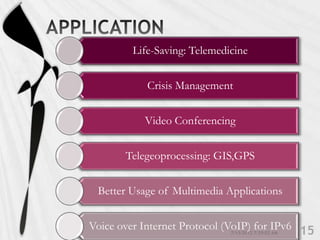
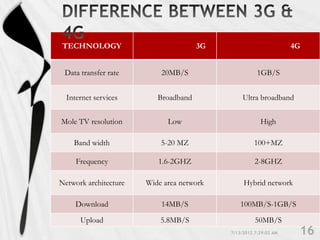
4G is the fourth generation of cellular network technology providing broadband Internet access. It aims to achieve ultra-broadband speeds in gigabits per second allowing users to download movies within 5 minutes. 4G uses packet switching and allows streaming of high-definition media to mobile devices. The first commercial 4G networks launched in Scandinavian countries in 2009. While some countries have started 4G, India is still working to fully implement 3G and likely won't deploy 4G until LTE technologies are more available. 4G will enable new mobile applications like telemedicine, video conferencing, and improved multimedia usage.