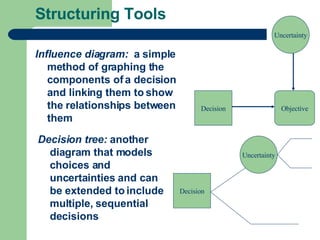
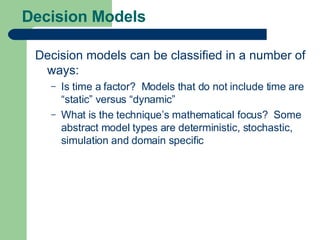
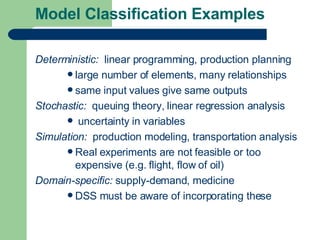
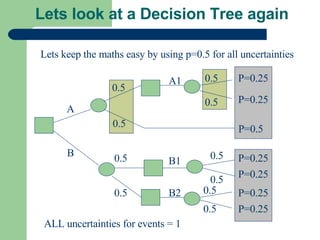
The document discusses key concepts in defining and structuring decision problems. It defines the three components of a problem statement as the current state, desired state, and central objective. Decision trees and influence diagrams are presented as tools to structure choices and uncertainties. Deterministic, stochastic, and simulation models are described based on their mathematical focus. Probability is discussed in terms of frequentist, subjective, and logical interpretations, and methods for forecasting and decomposing complex probabilities are outlined. Calibration and sensitivity analysis are introduced as ways to evaluate probability estimates and assumptions.