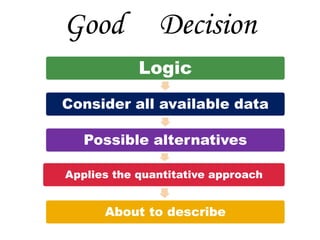
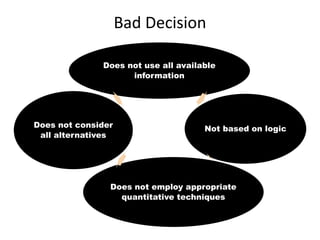
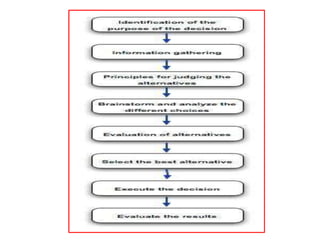
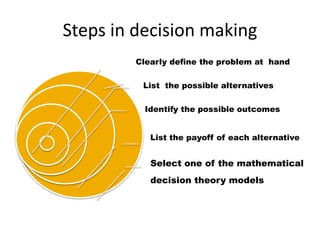
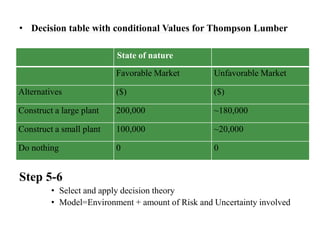
The document discusses decision analysis and outlines the steps involved in making good decisions, including clearly defining the problem, listing alternatives and outcomes, evaluating alternatives using decision models, and selecting the best alternative. It provides an example of a lumber company evaluating whether to expand its product line by manufacturing backyard storage sheds, walking through the steps of defining the problem, listing alternatives, assessing potential profits in favorable and unfavorable market conditions, and selecting the optimal alternative using a decision table.