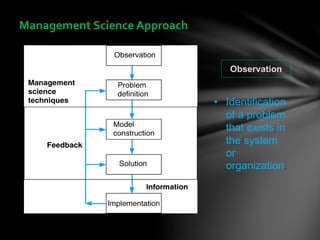
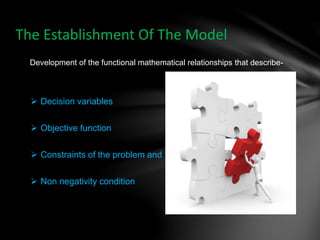
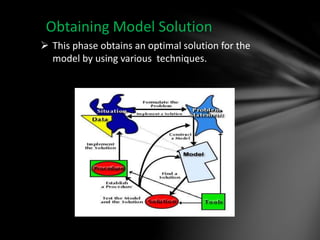
Operations research is a scientific approach to decision making that was developed during World War II and is now used widely in business and industry. It involves defining problems quantitatively and building mathematical models to represent real-world situations. These models are used to evaluate alternative solutions systematically and predict outcomes in order to optimize decisions. The process involves identifying problems, developing models, obtaining optimal solutions using techniques like linear programming, testing the model solutions, and implementing the best solution. Operations research helps organizations make more informed decisions using data, consider all options, and manage resources effectively.