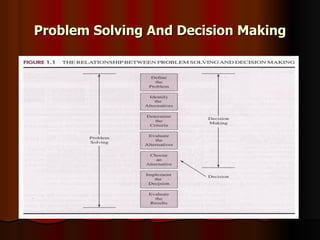
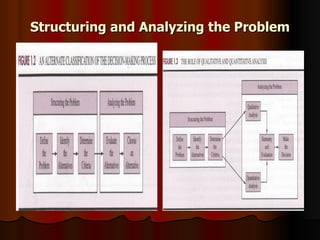
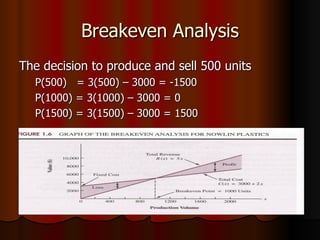
This document provides an introduction to management science, including definitions of management science, problem solving, and decision making. It discusses quantitative analysis techniques in management science like modeling, data preparation, model solution, and conclusion/reporting. Specific models discussed include cost, revenue, profit, and breakeven analysis. Finally, it lists some common management science techniques and software.