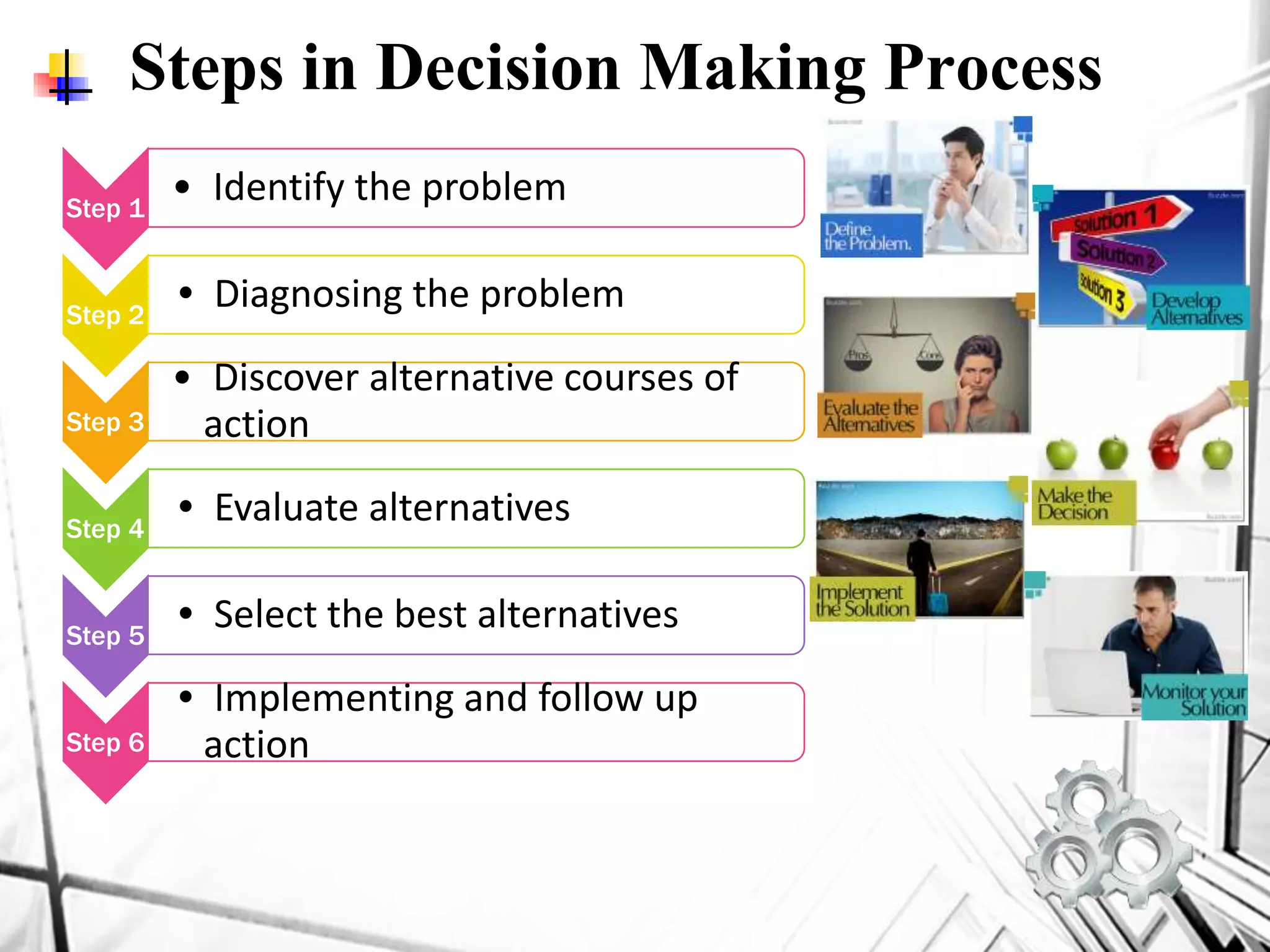
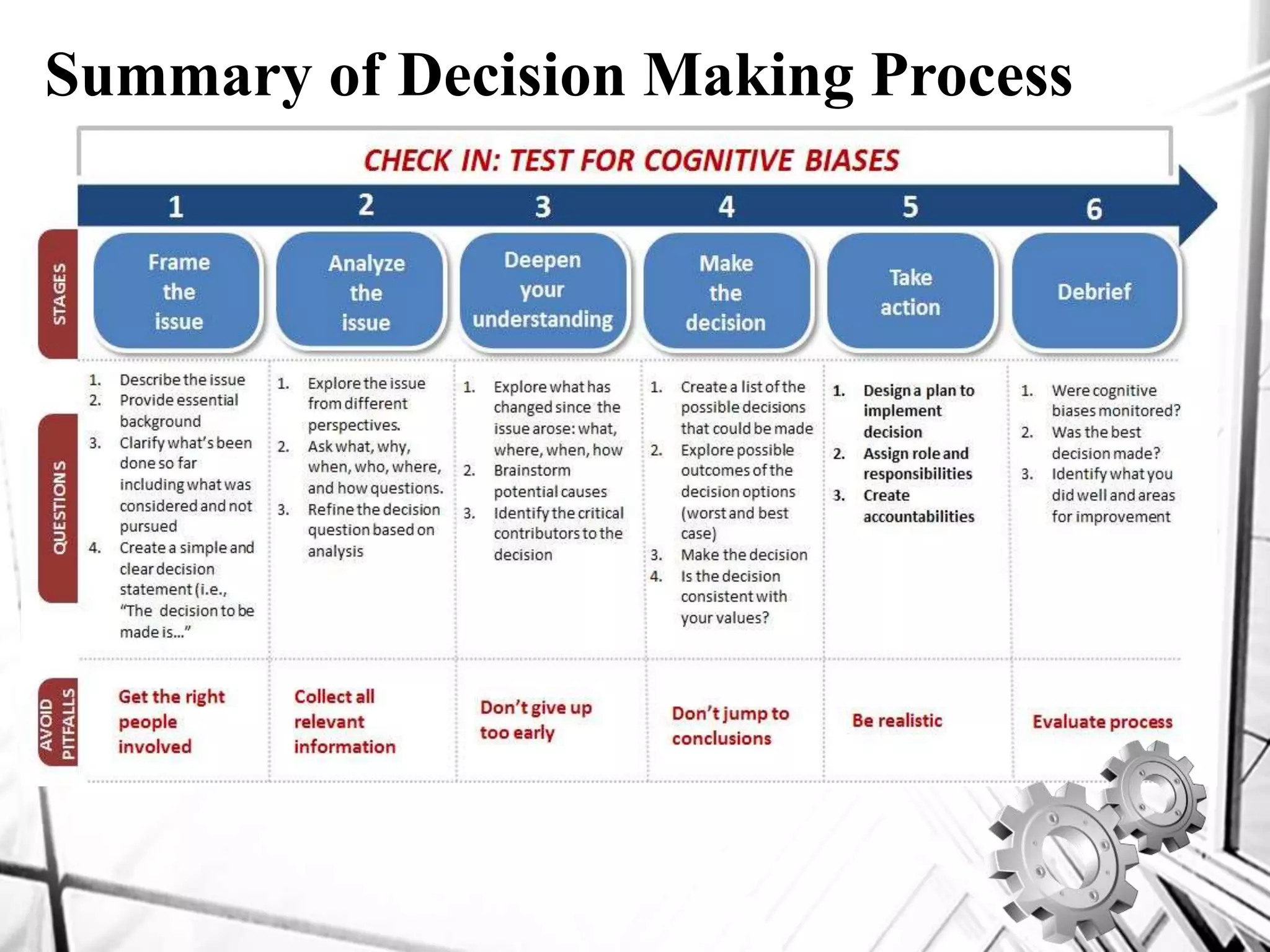
The 6 step decision making process involves: 1) identifying the problem, 2) diagnosing the problem through analysis from different perspectives, 3) discovering alternative courses of action through research and creativity, 4) evaluating alternatives by considering advantages and disadvantages, 5) selecting the best alternative, and 6) implementing and following up on the decision through evaluation of results.