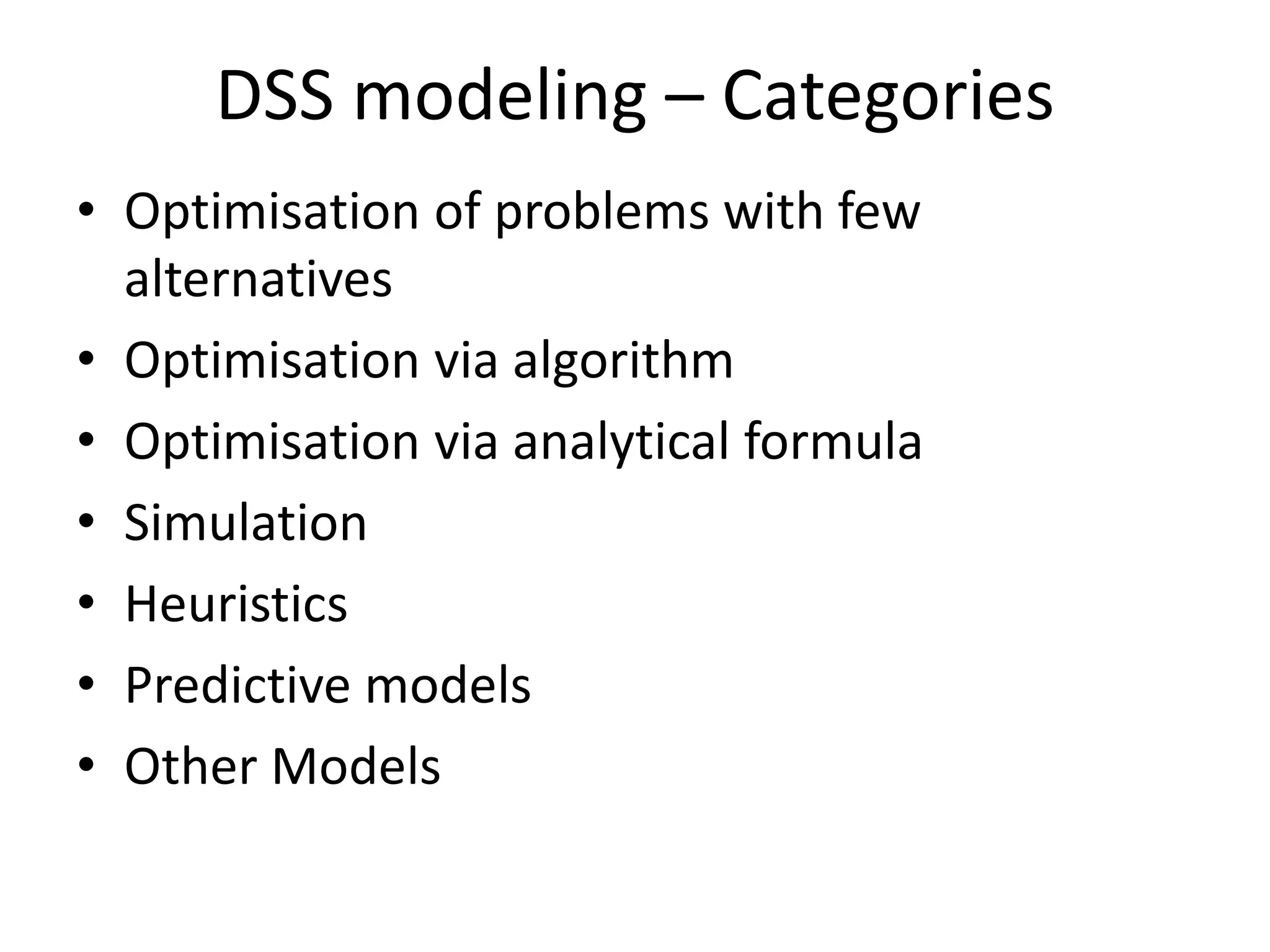
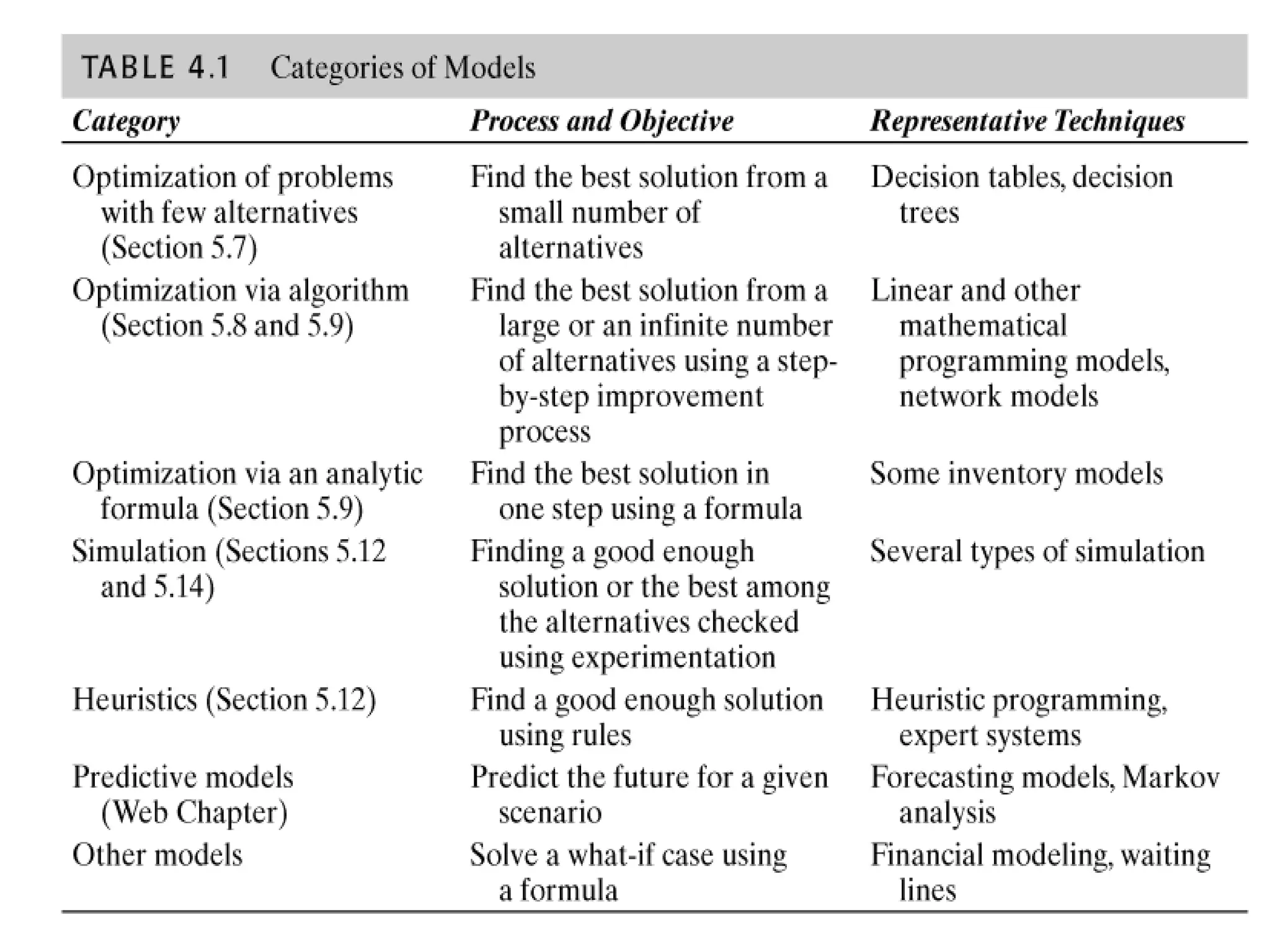
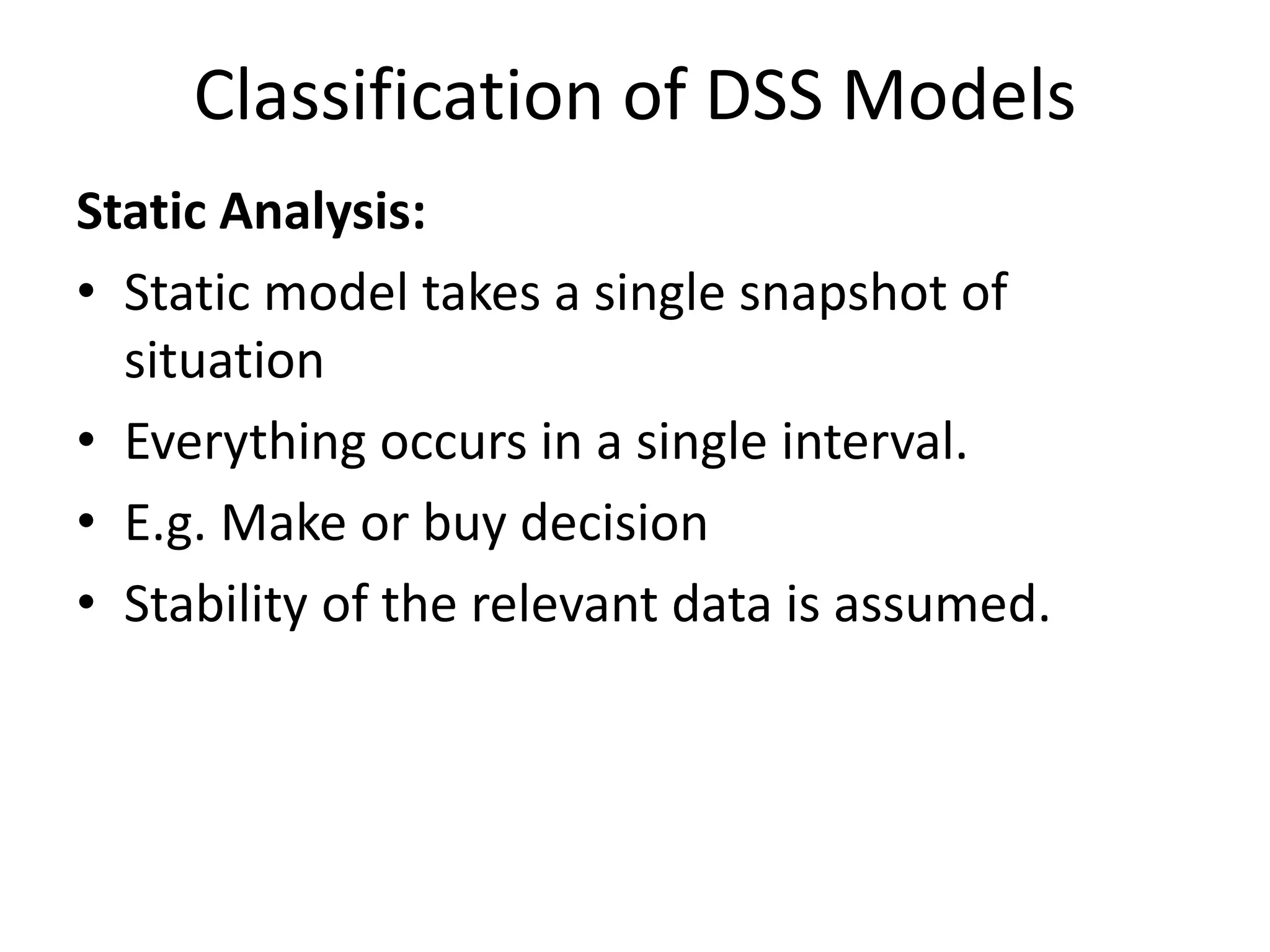
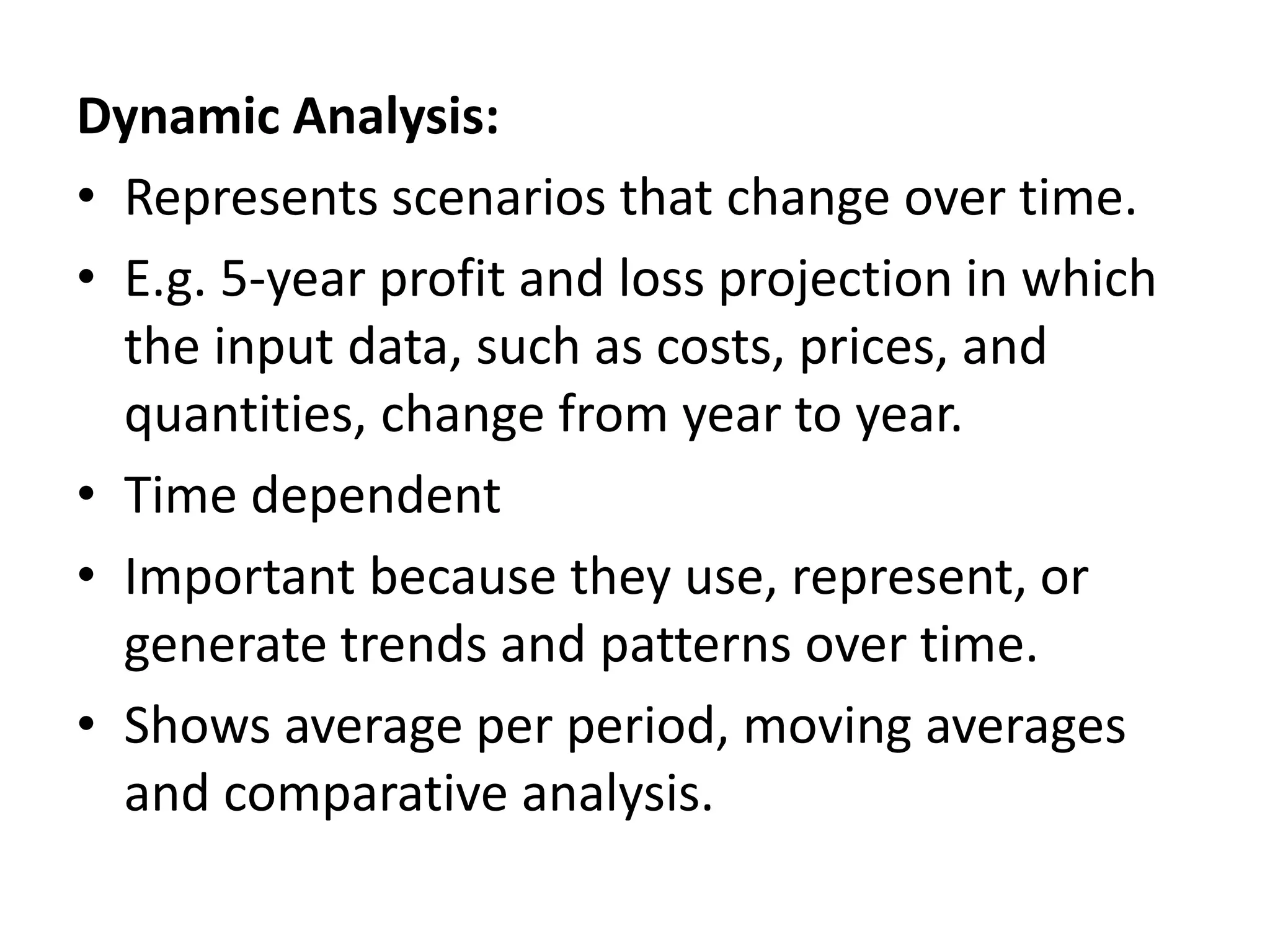
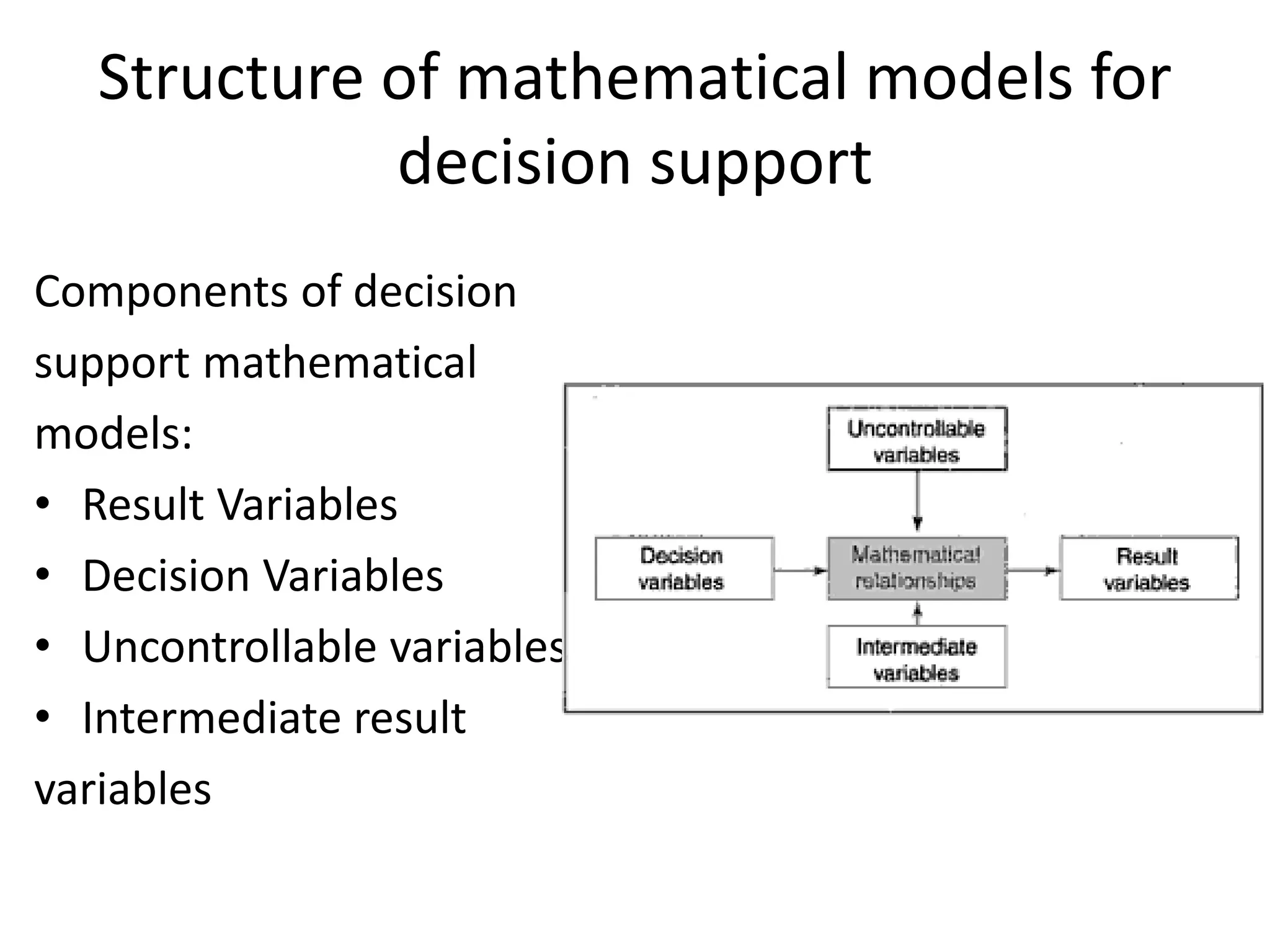
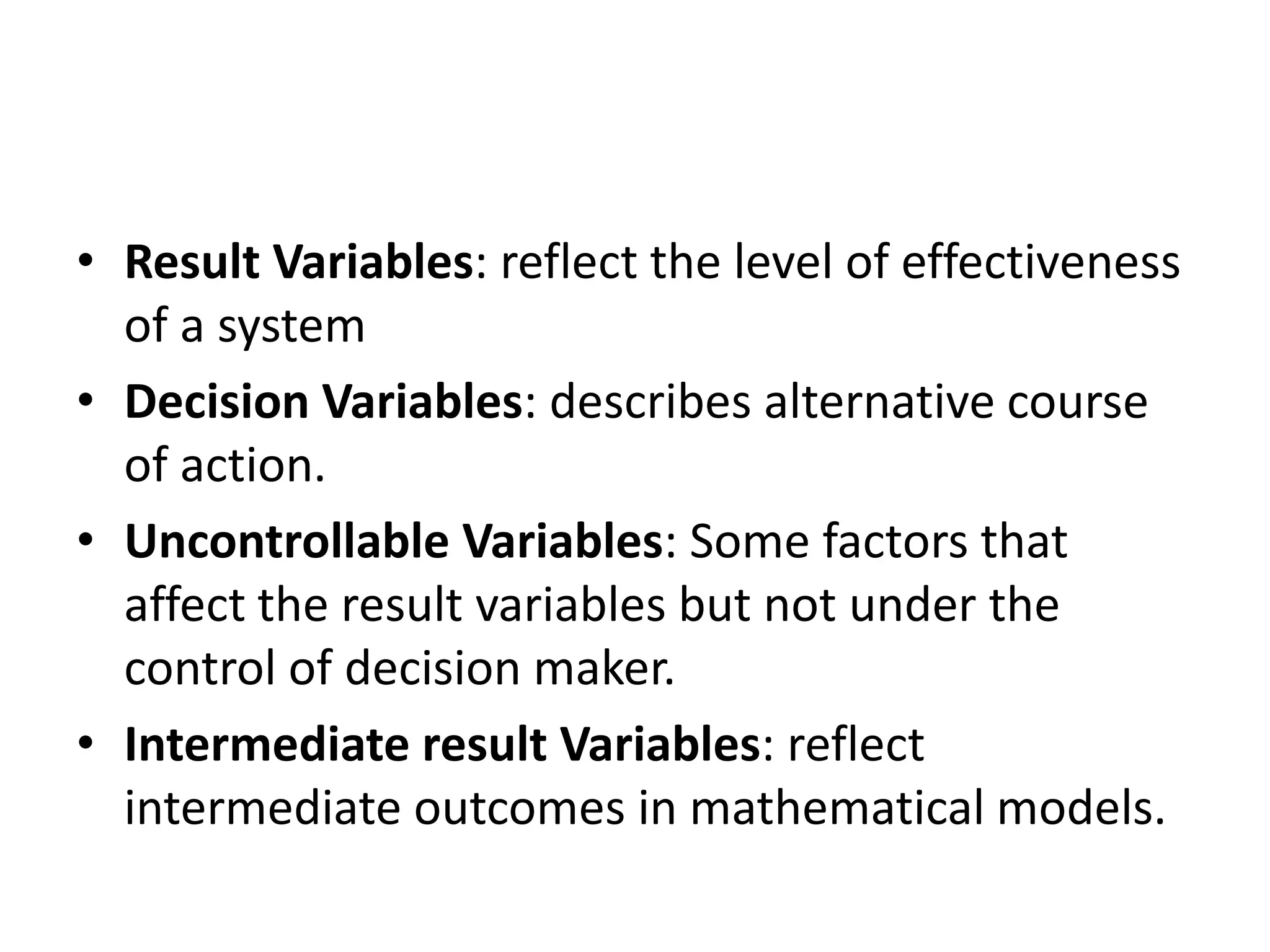
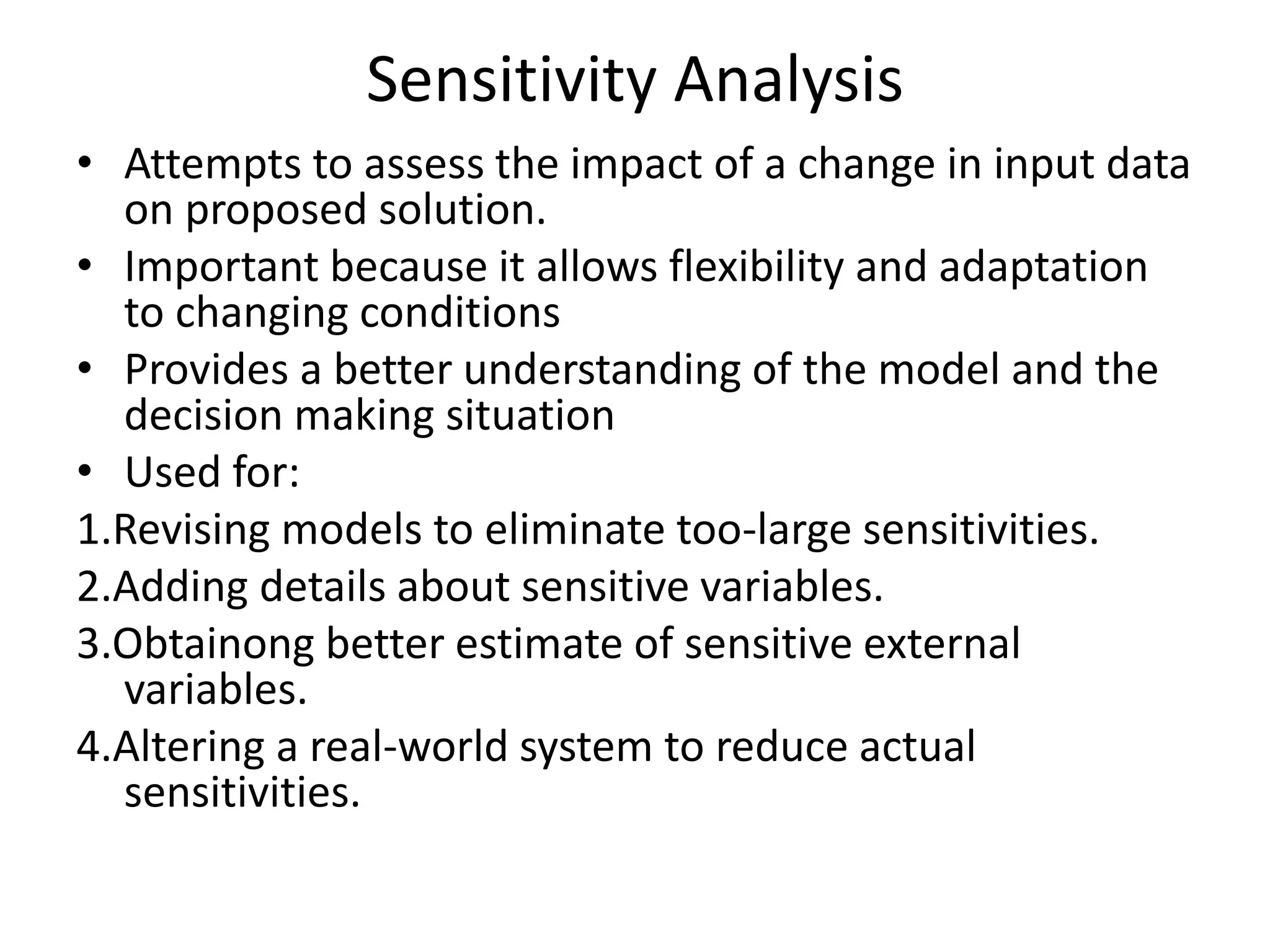
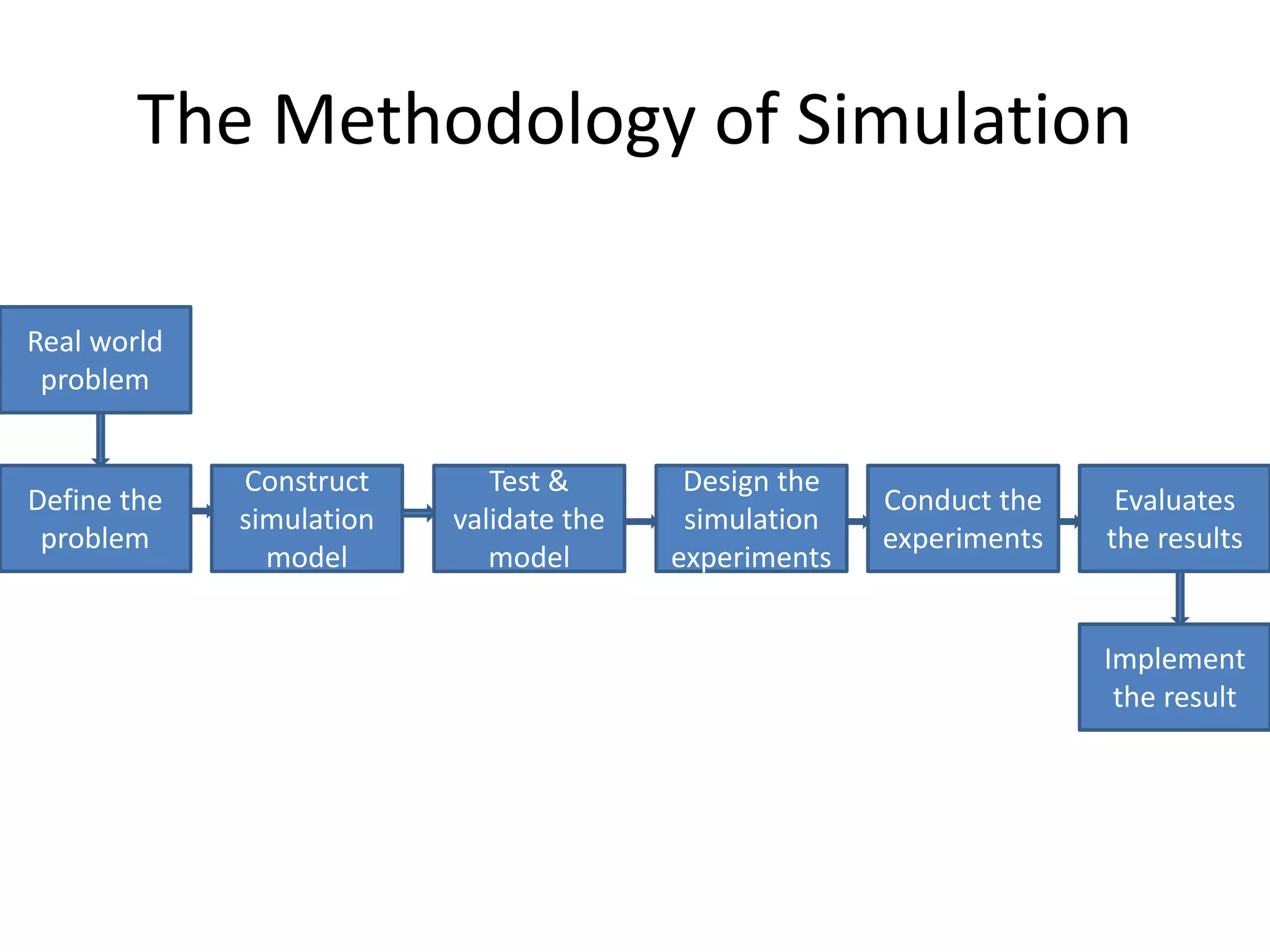
This document discusses modeling and analysis techniques used in decision support systems (DSS). It covers various categories of DSS models including optimization, simulation, and predictive models. It also describes static and dynamic analysis, decision making under certainty, risk, and uncertainty. Different modeling approaches like mathematical modeling, simulation, and heuristics are explained.