The document provides an overview of business decision making. It discusses key concepts such as the types of decisions managers make, the decision-making process, models of decision making, and tools that can be used. Some of the main points covered include:
- Managers are responsible for making independent decisions to efficiently execute organizational functions.
- Decision-making involves selecting the best alternative from multiple options to solve problems like crises, opportunities, or routine issues.
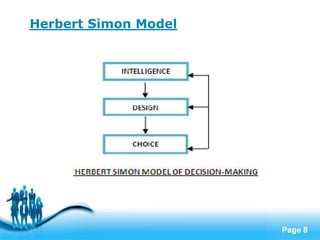
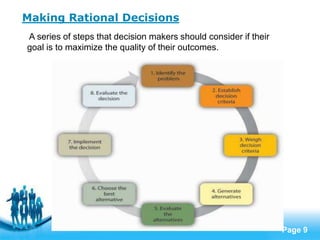
- Models of rational decision making assume managers logically choose alternatives to maximize goals, though bounded rationality recognizes limits to rationality.
- Quantitative and qualitative tools can help structure decision making, including techniques like marginal analysis, decision trees, and brainstorming