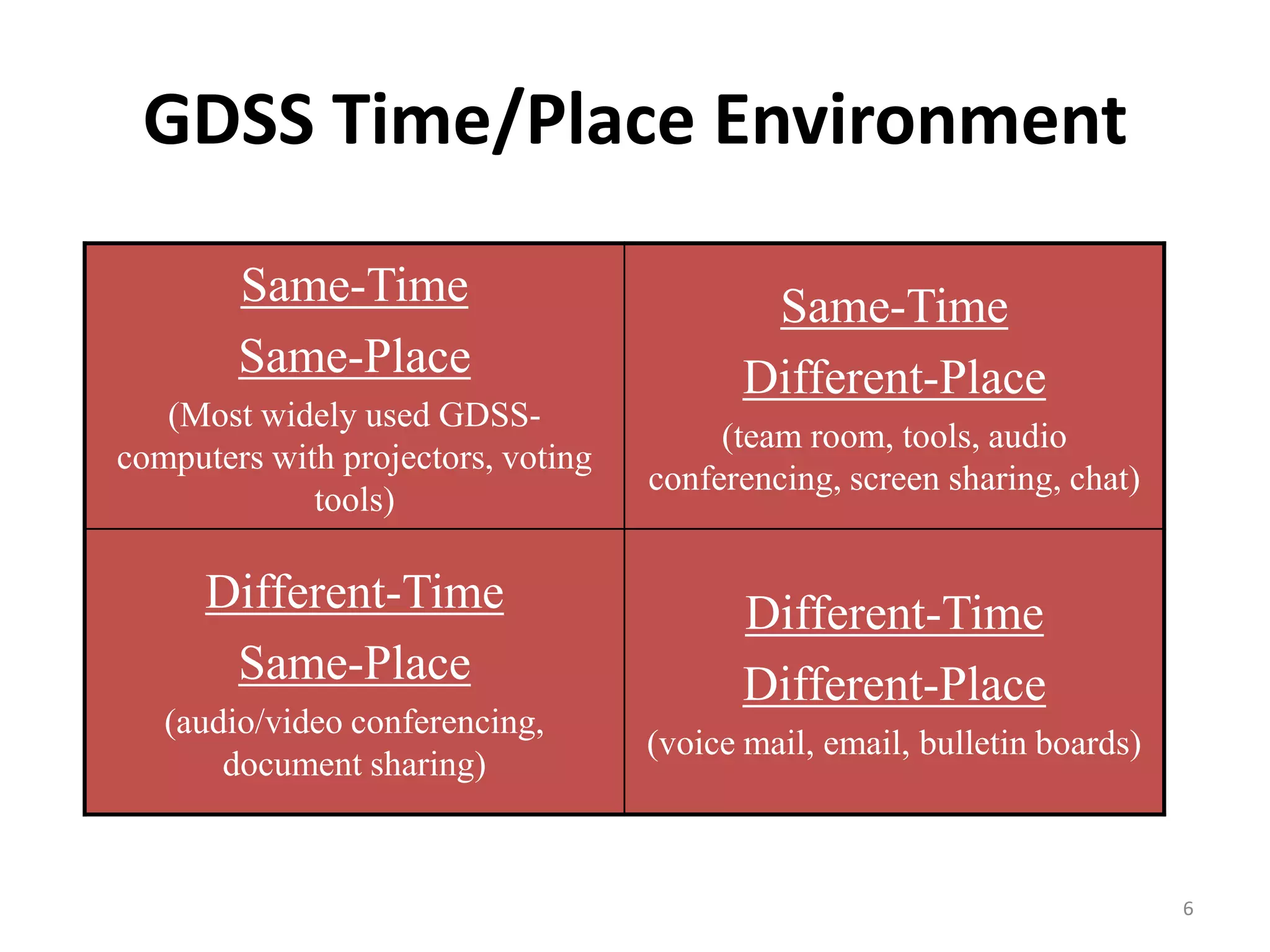
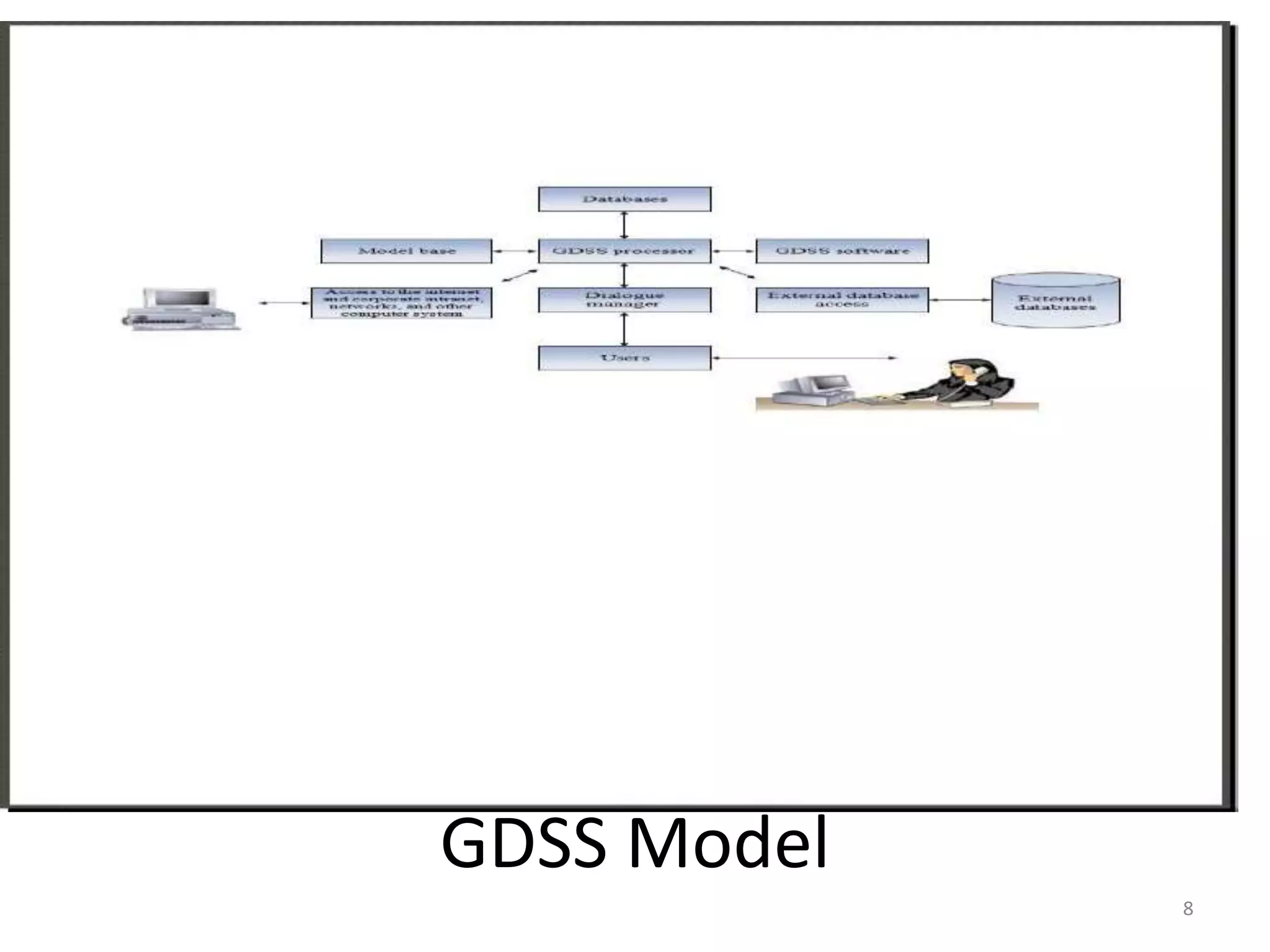
Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) are electronic meeting systems focused on enhancing group decision-making processes through specific hardware, software, and procedures. They facilitate improved communication and participation among decision-makers while providing advantages such as reduced decision time and global connectivity. However, GDSS also faces challenges related to costs, security, technical failures, and user training.